EIN Civil Society Briefing March 2024 - Greece, Türkiye, Moldova and Italy
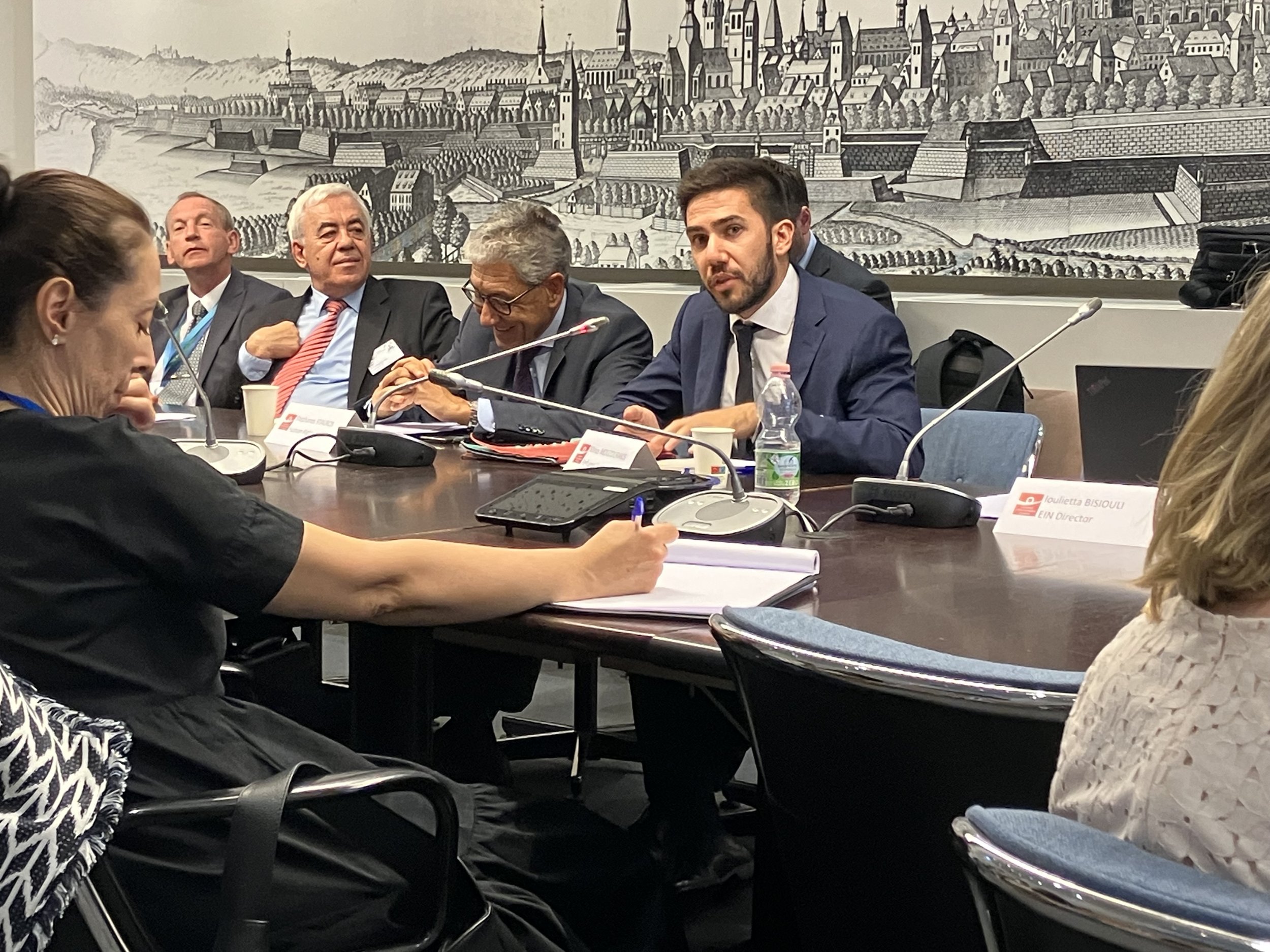
/On the 1st of March 2024, EIN held the latest civil society briefing for permanent Representations of the Council of Europe, ahead of the 1492nd Committee of Ministers Human Rights Meeting which takes place between 12th – 14th March 2024. The event was held in person in Strasbourg, and facilitated by Ioulietta Bisiouli, EIN Director.
The Briefing focused on the following cases:
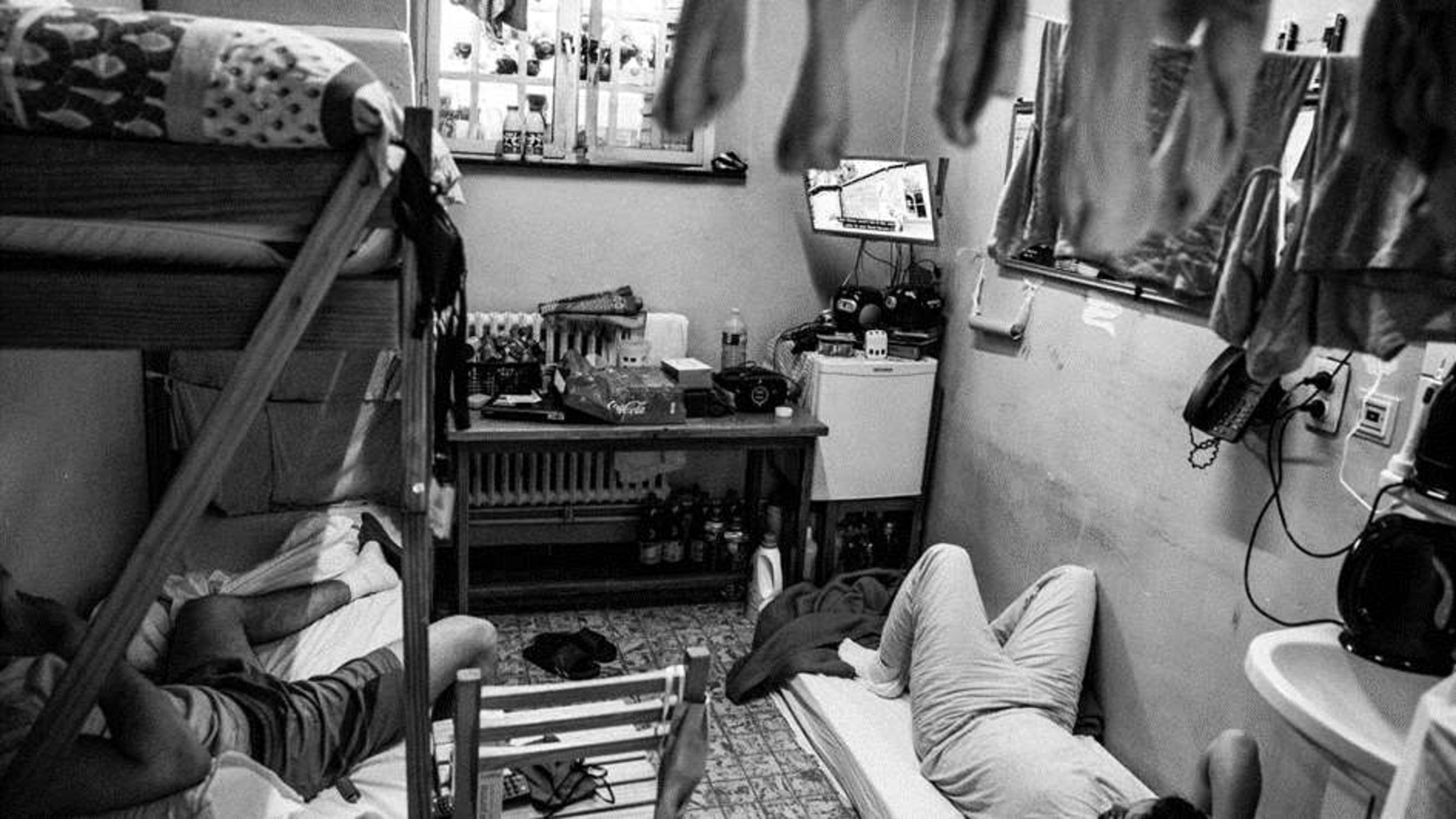
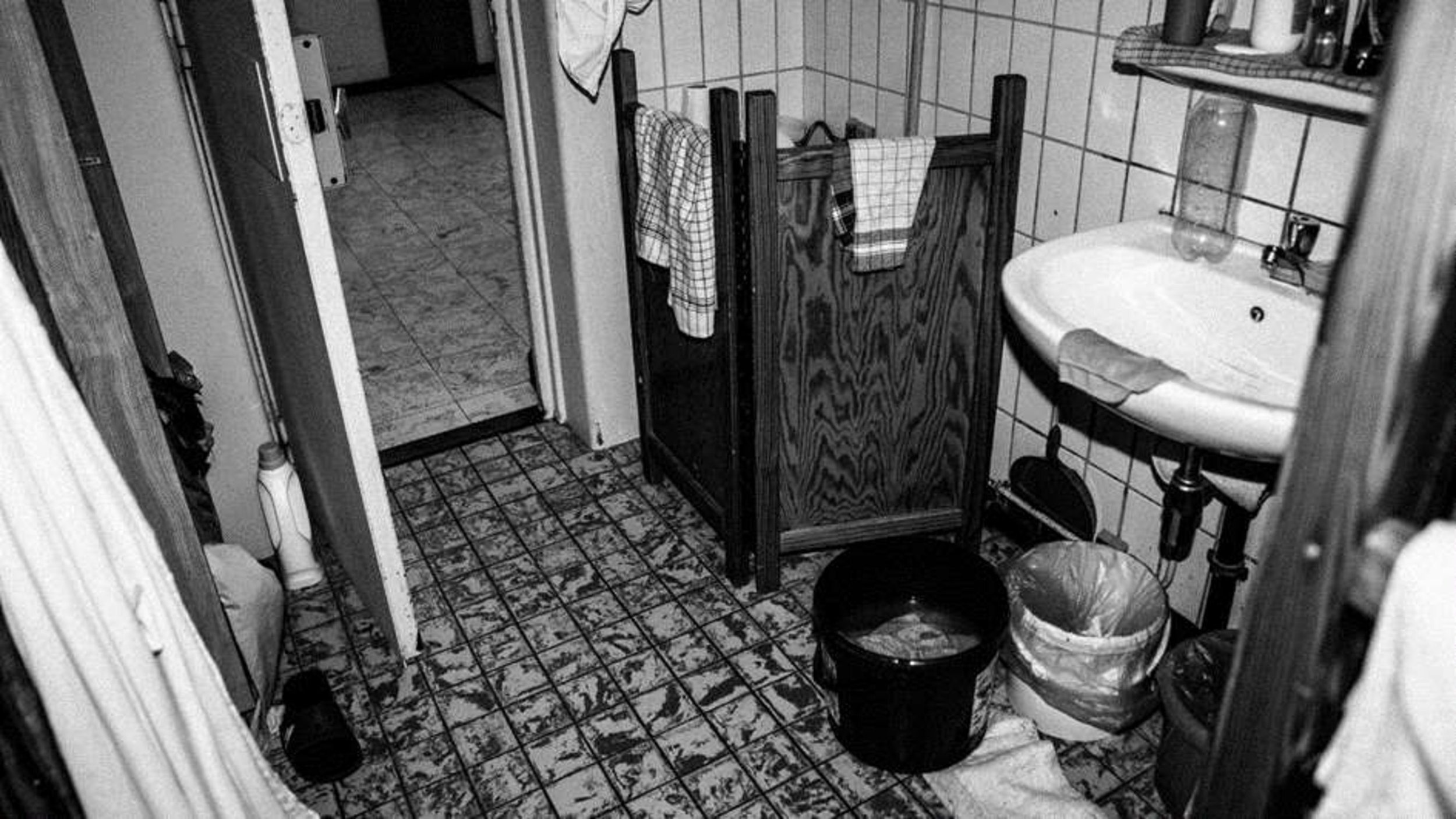
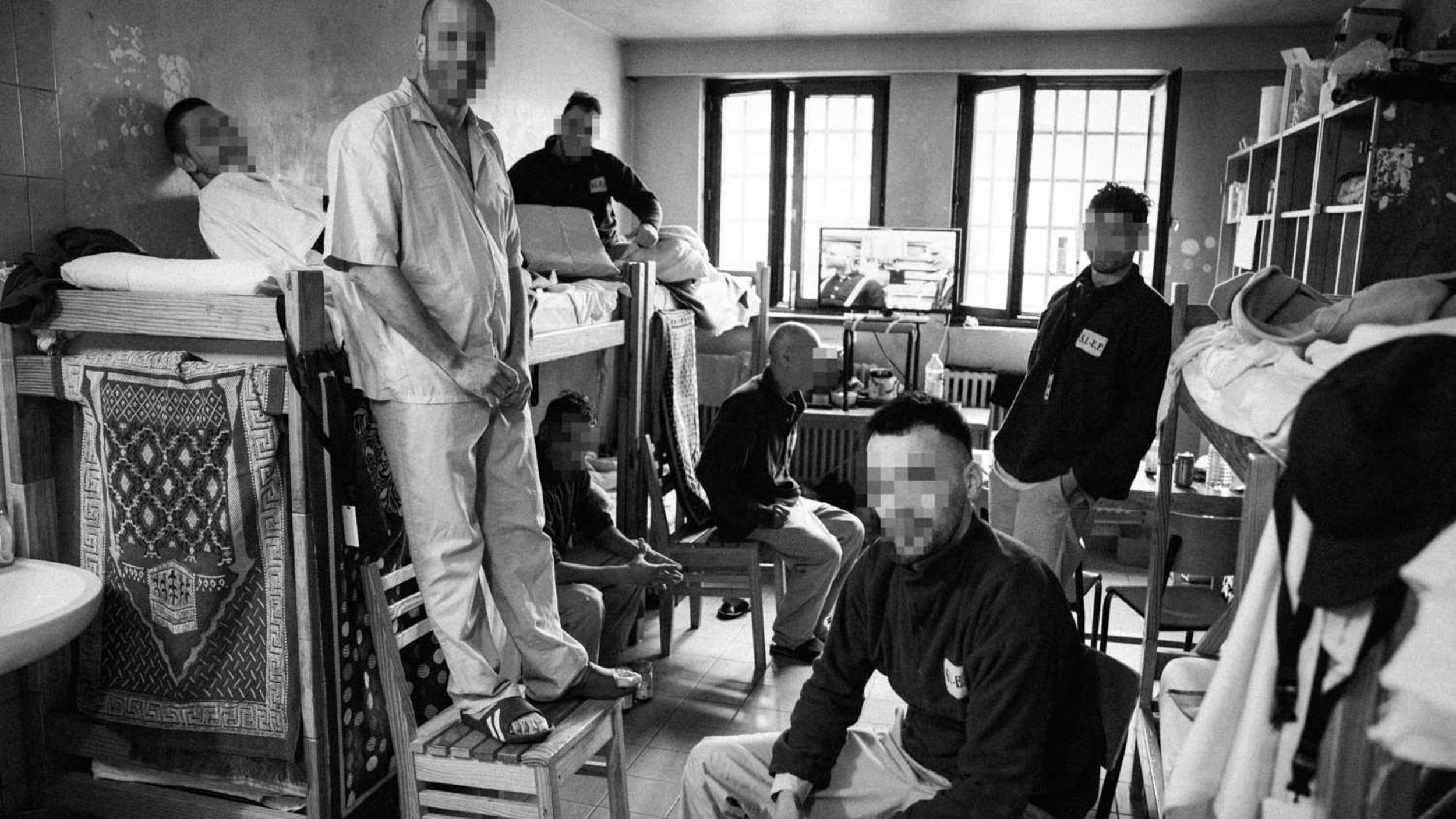
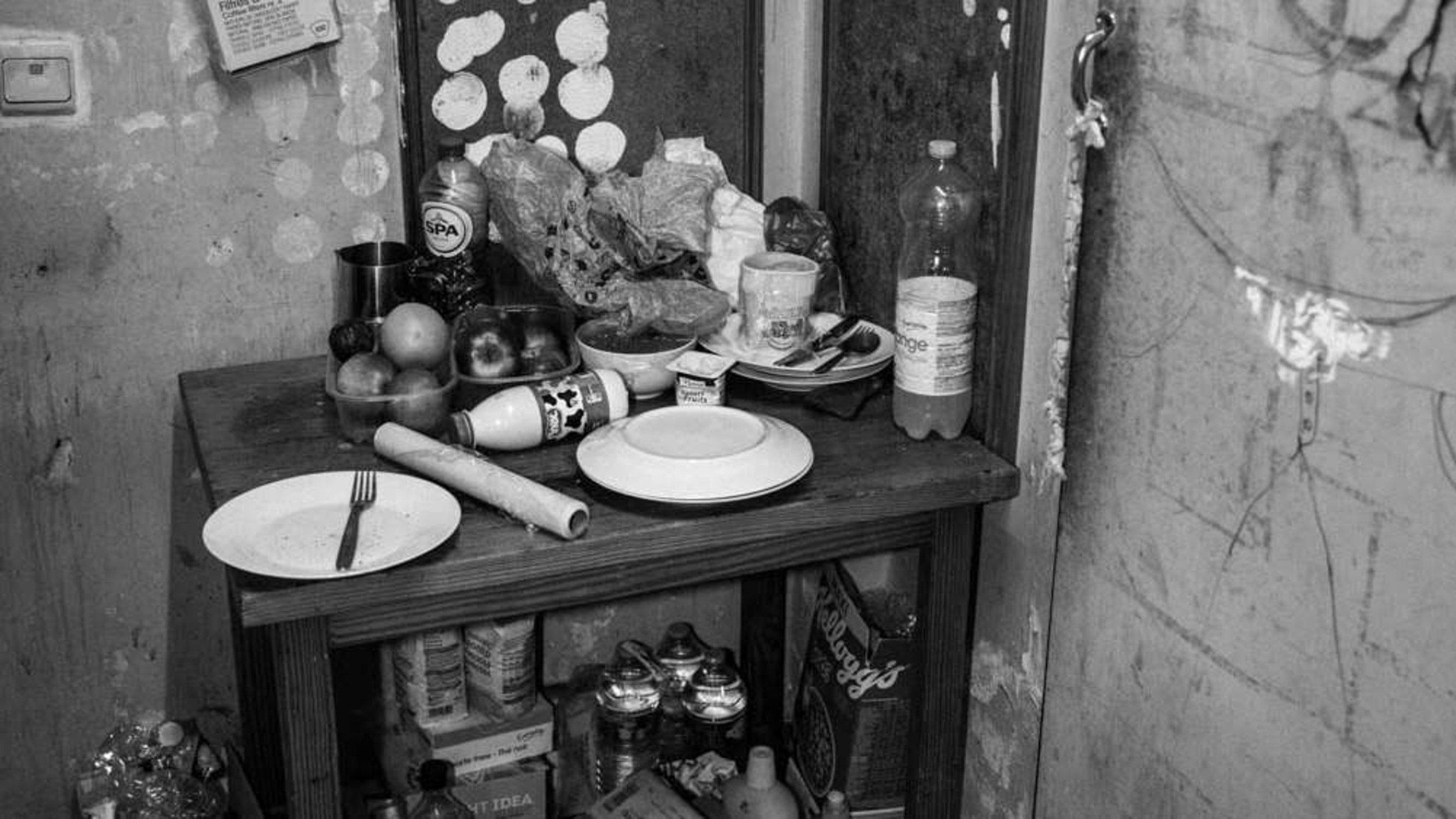
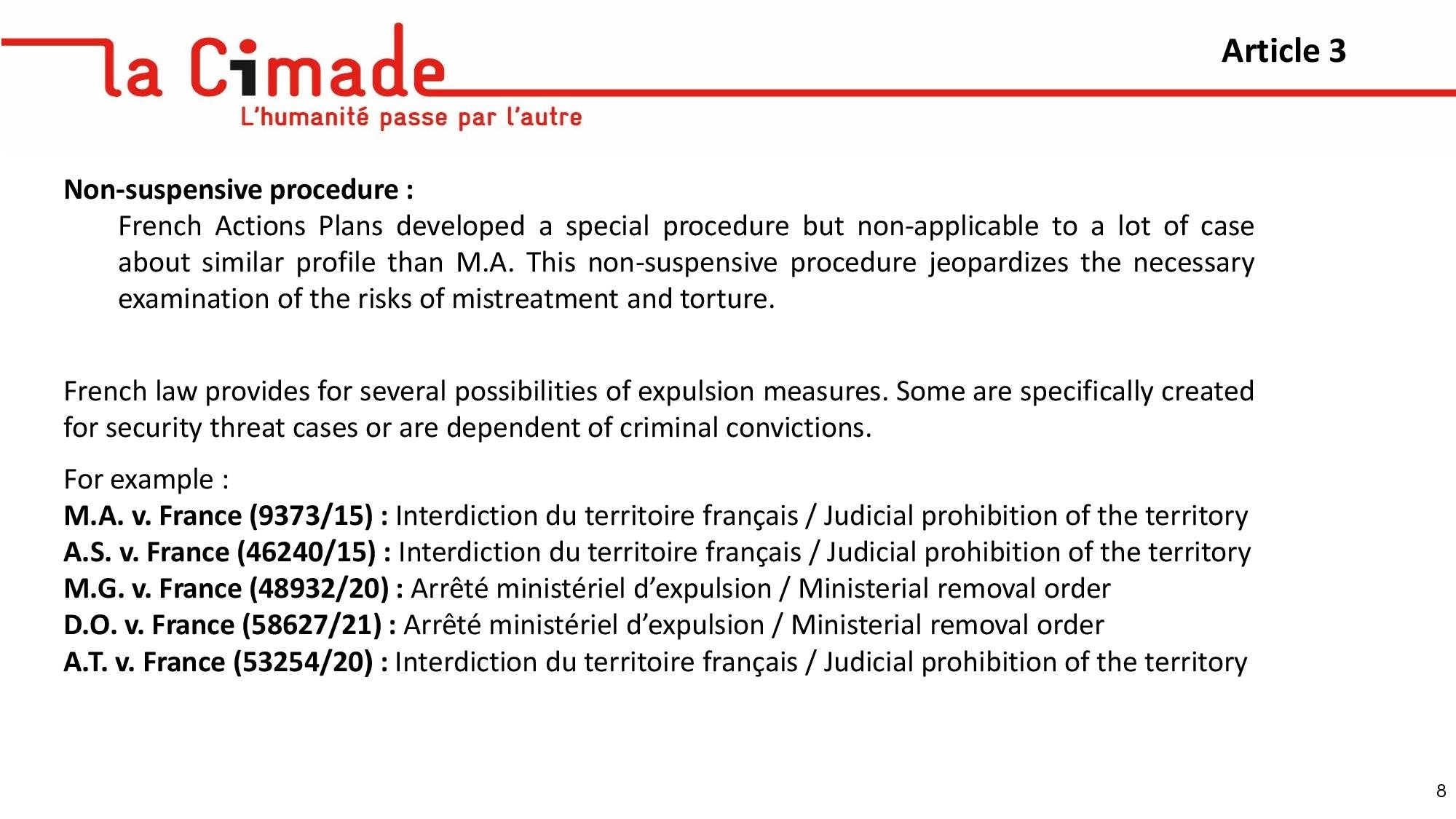
Nisiotis Group v Greece, which concerns prison overcrowding and other poor conditions in prison and the lack of effective remedy, presented by Prof. Konstantinos Tsitselikis, representative of the Hellenic League for Human Rights.
Öner and Turk v Türkiye, Işıkırık v Türkiye, Altuğ Taner Akçam v Türkiye, Artun and Güvener v Türkiye and Nedim Şener v Türkiye groups, which concern the unjustified interferences with freedom of expression, in particular through criminal proceedings, including defamation, and the consequent chilling effect, as well as unforeseeable conviction of membership of an illegal organisation for the mere fact of attending a public meeting and expressing views there, presented by Batıkan Erkoç, Project and Grants Manager at MLSA, Özlem Zingil and Idil Özcan, Program Director and Lawyer at Hafiza Merkezi.
Manole and others v the Republic of Moldova, which concerns censorship and political control by State authorities at State Television Company, Teleradio-Moldova, presented by Cristina Frumosu-Durnea, Media Lawyer, Independent Journalism Centre.
Darboe and Camara v Italy, which concerns placement of unaccompanied minor in adult reception centre in inadequate conditions and without being provided with minimum procedural guarantees in age-assessment procedure by Elena Rozzi, Lawyer at ASGI.
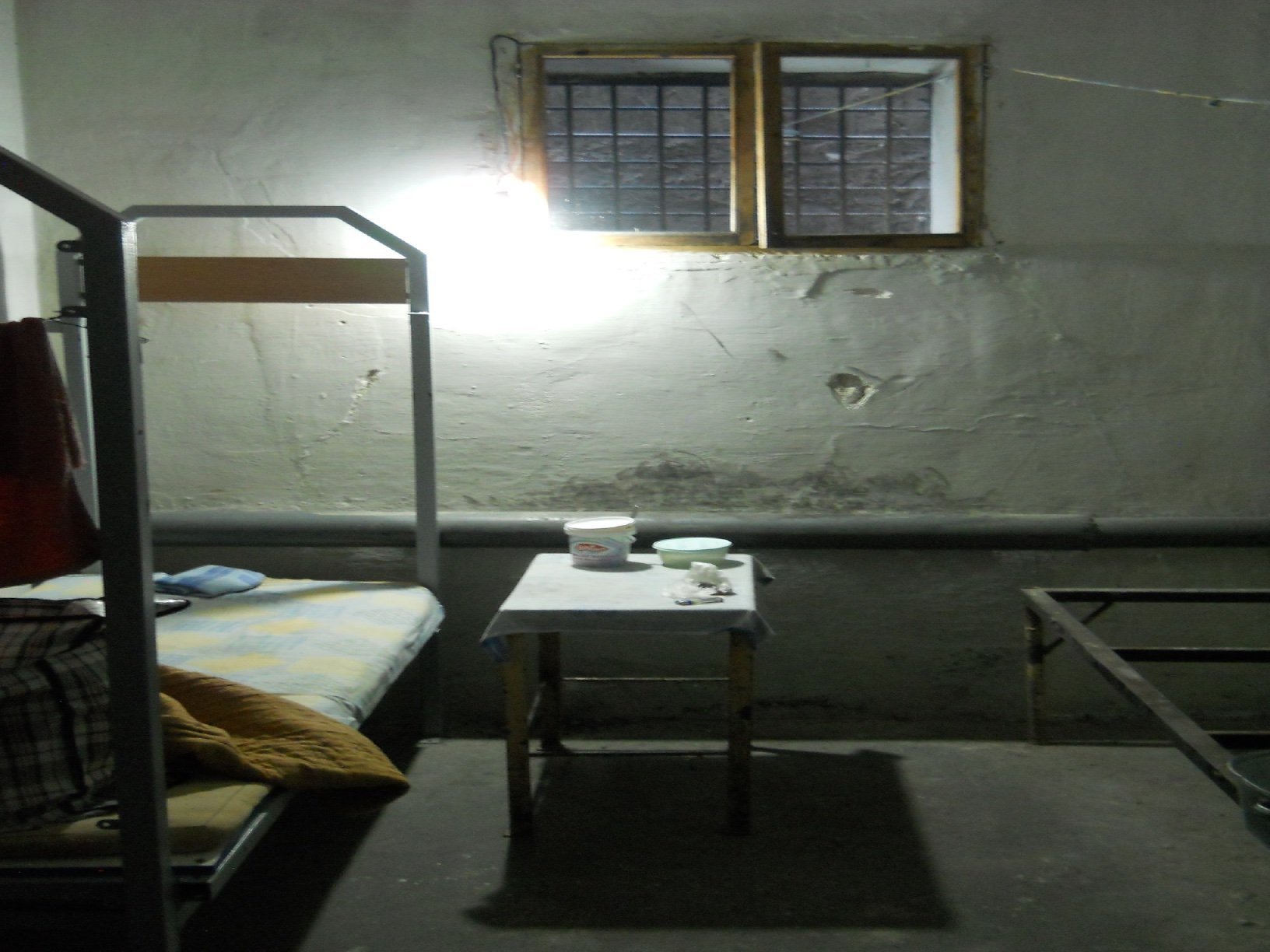
The Nisiotis Group v Greece group of cases concern the inhuman and/or degrading treatment of the applicants on account of the poor conditions of detention of the applicants in overcrowded prisons in Greece (violations of Article 3). The findings in the cases in this group include: overpopulation in prisons; inadequate medical services in prison; deficiencies in infrastructure: lack of dinning place, inadequate ventilation, lack of toilet doors, inadequate heating, as well as the lack of an effective remedy in respect of the applicants’ complaints concerning the conditions of their detention (Article 13).
Hellenic League for Human Rights highlighted major findings of the Convention for the Prevention of Torture (CPT) in respect of Greece:
Prison conditions and Overpopulation and Understaffing – untrained staff.
No effective complaints system.
Lack of a long-term policy and a strategic plan.
Inter-prisoner violence.
Transfer of prisoners by police vehicles.
Ref: CPT report 2022 and CPT report 2023
Hellenic League for Human Rights discussed current trends and obstacles:
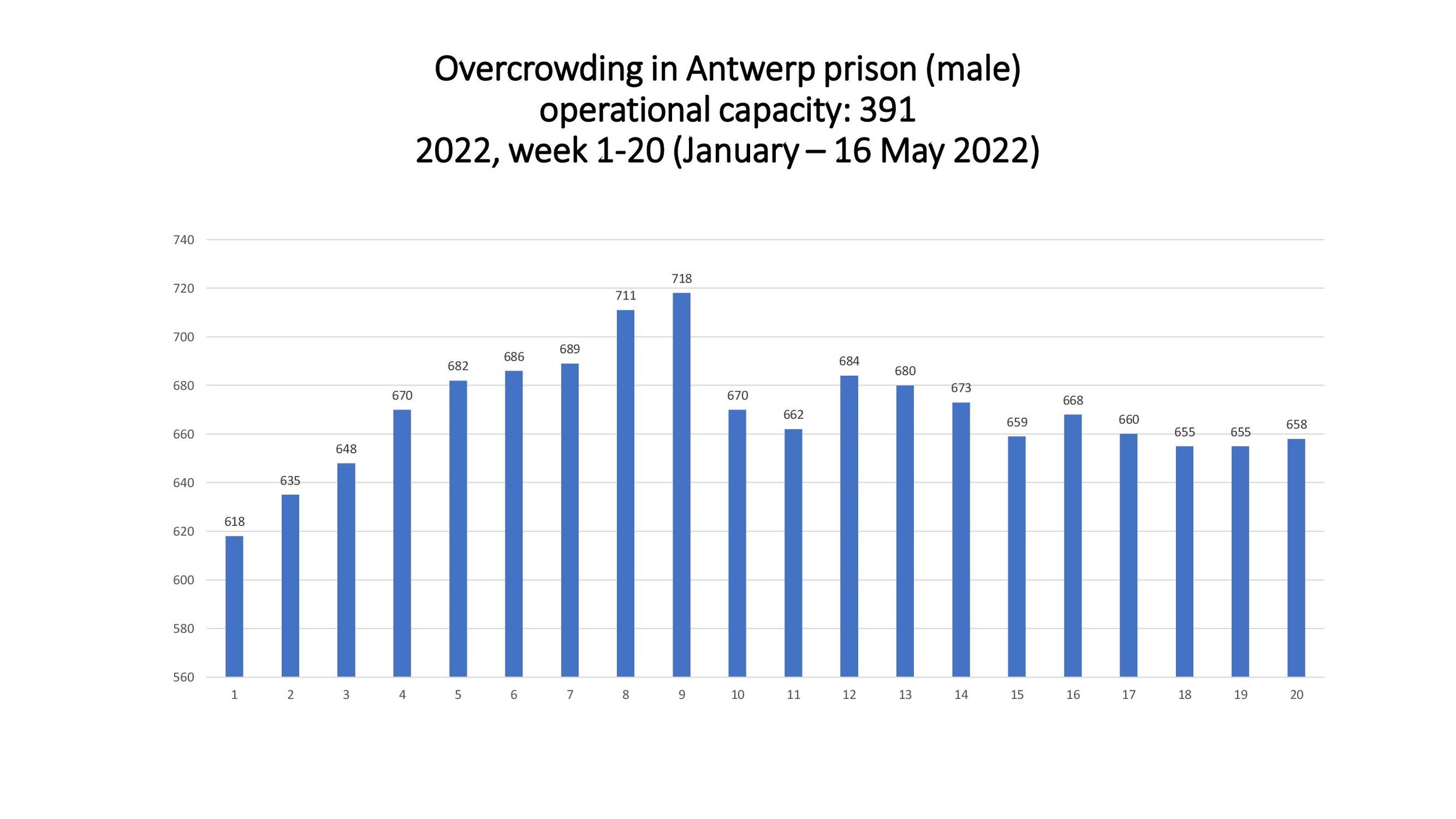
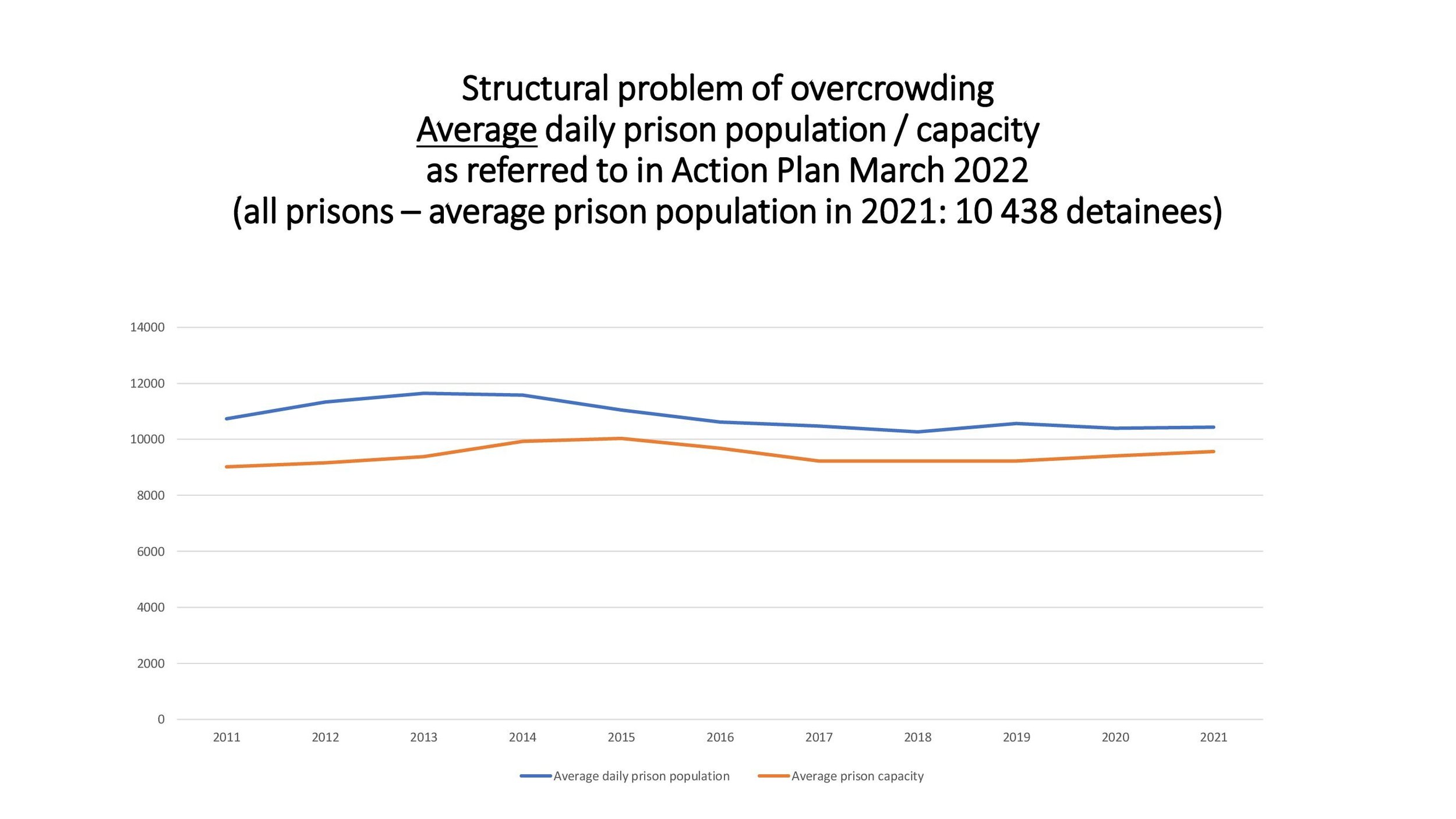
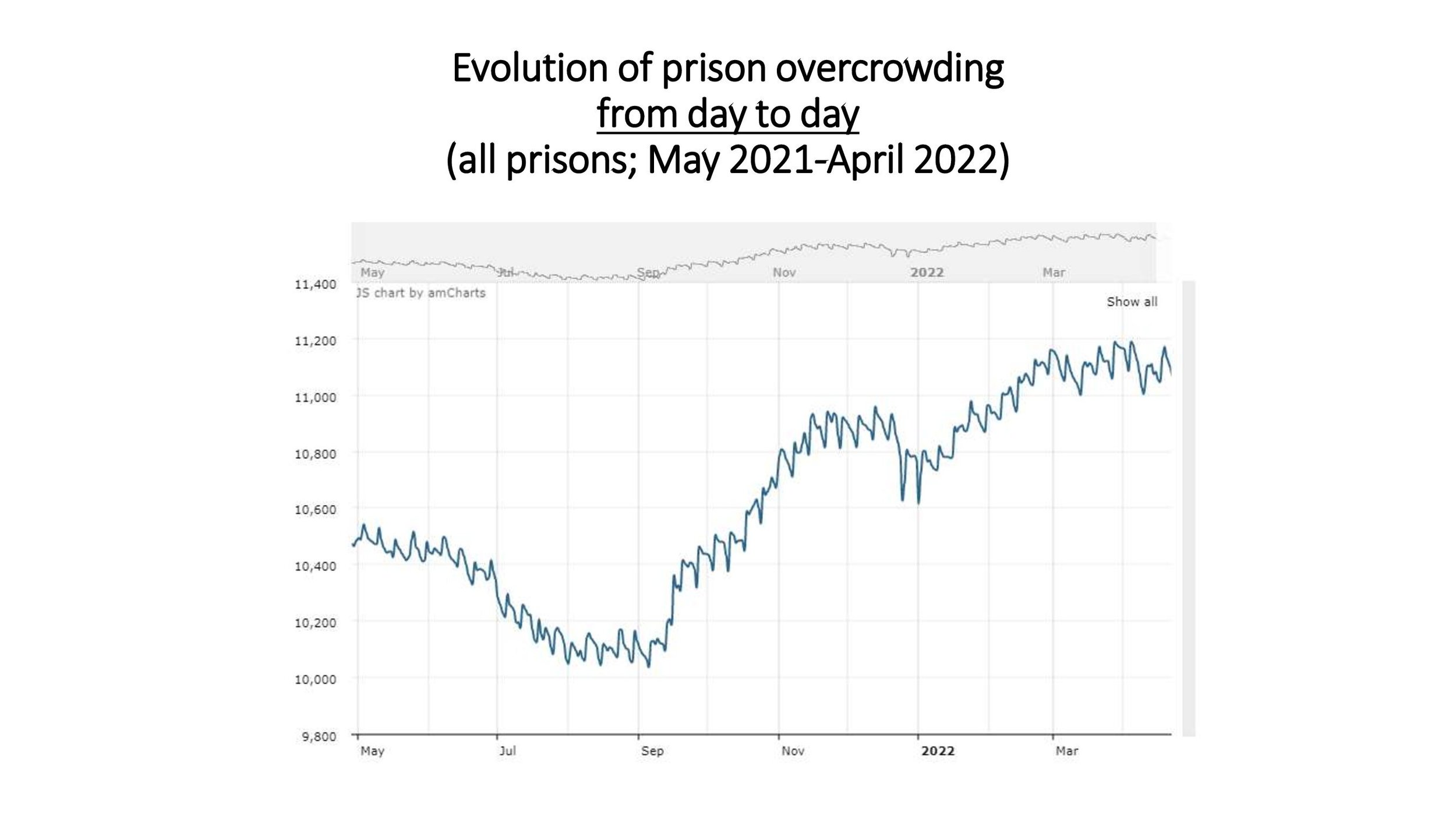
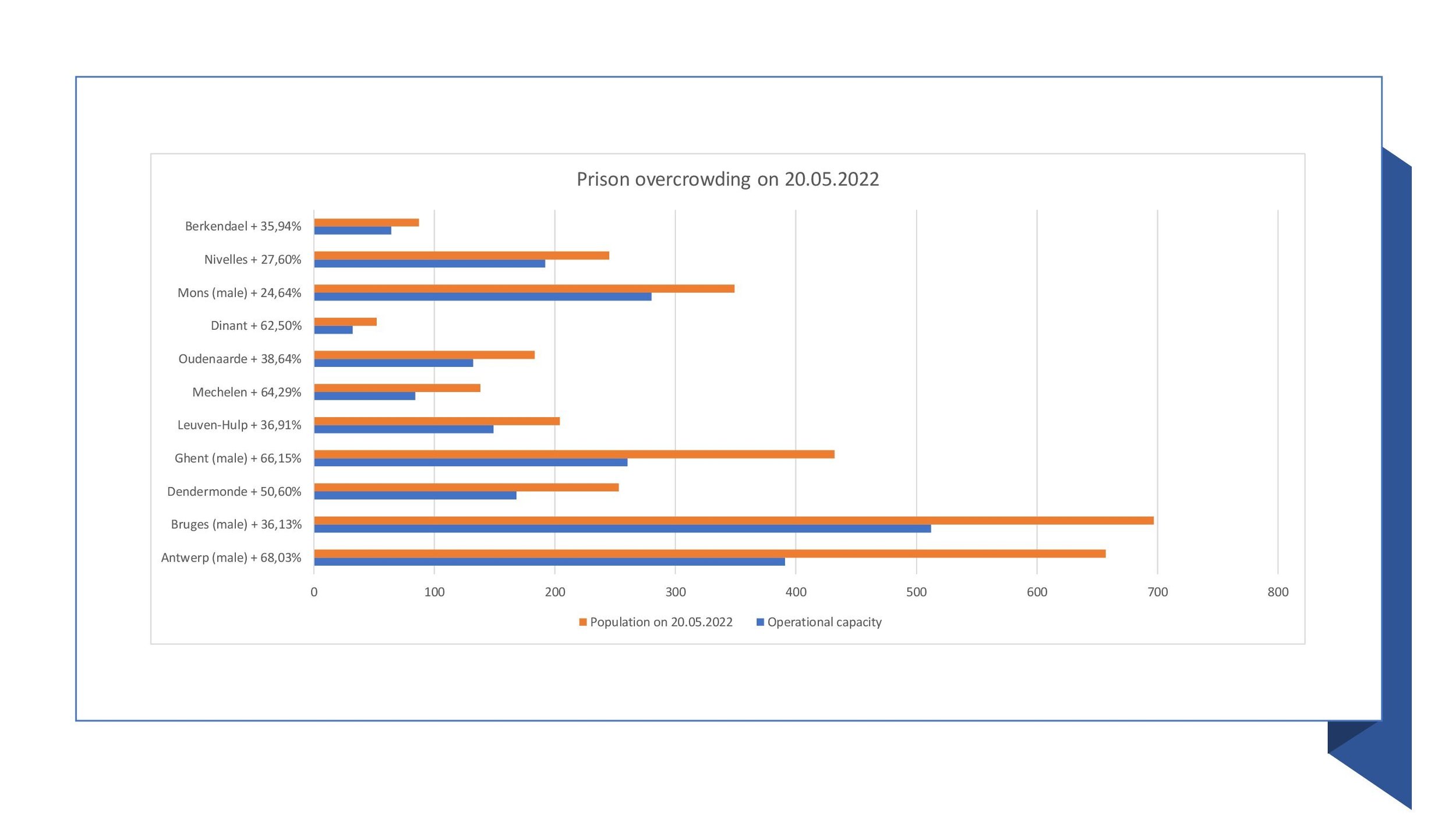
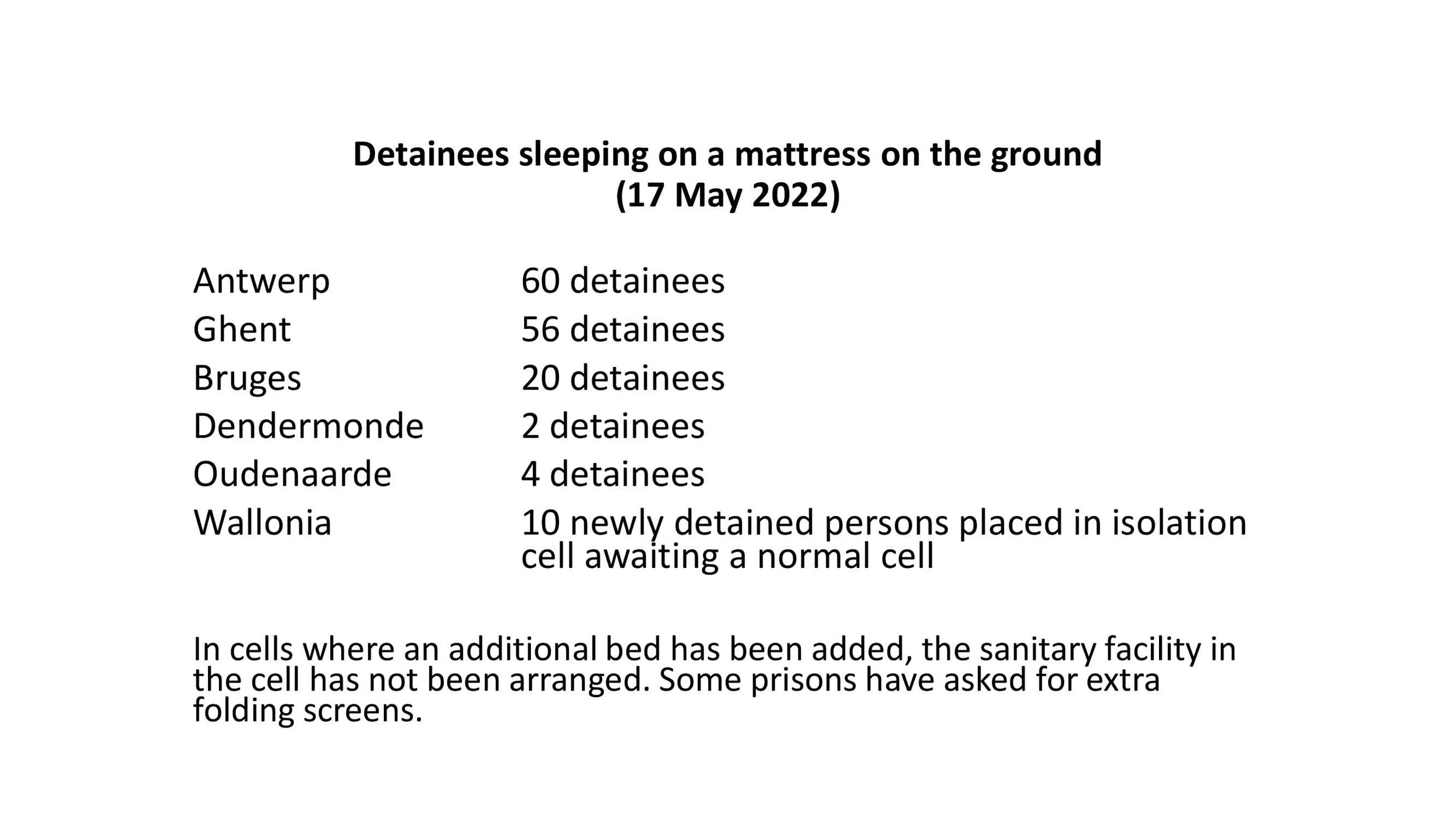
Prison population is at 10,270. All closed prison establishments suffer from extreme occupancy that constantly exceeds maximum capacity.
Average occupancy of closed prisons: 120-160%
Average occupancy of open prisons: 35-60%
No social work and minimal to no use of monitoring bracelet
Hellenic League for Human Rights addressed what the Greek government has done so far:
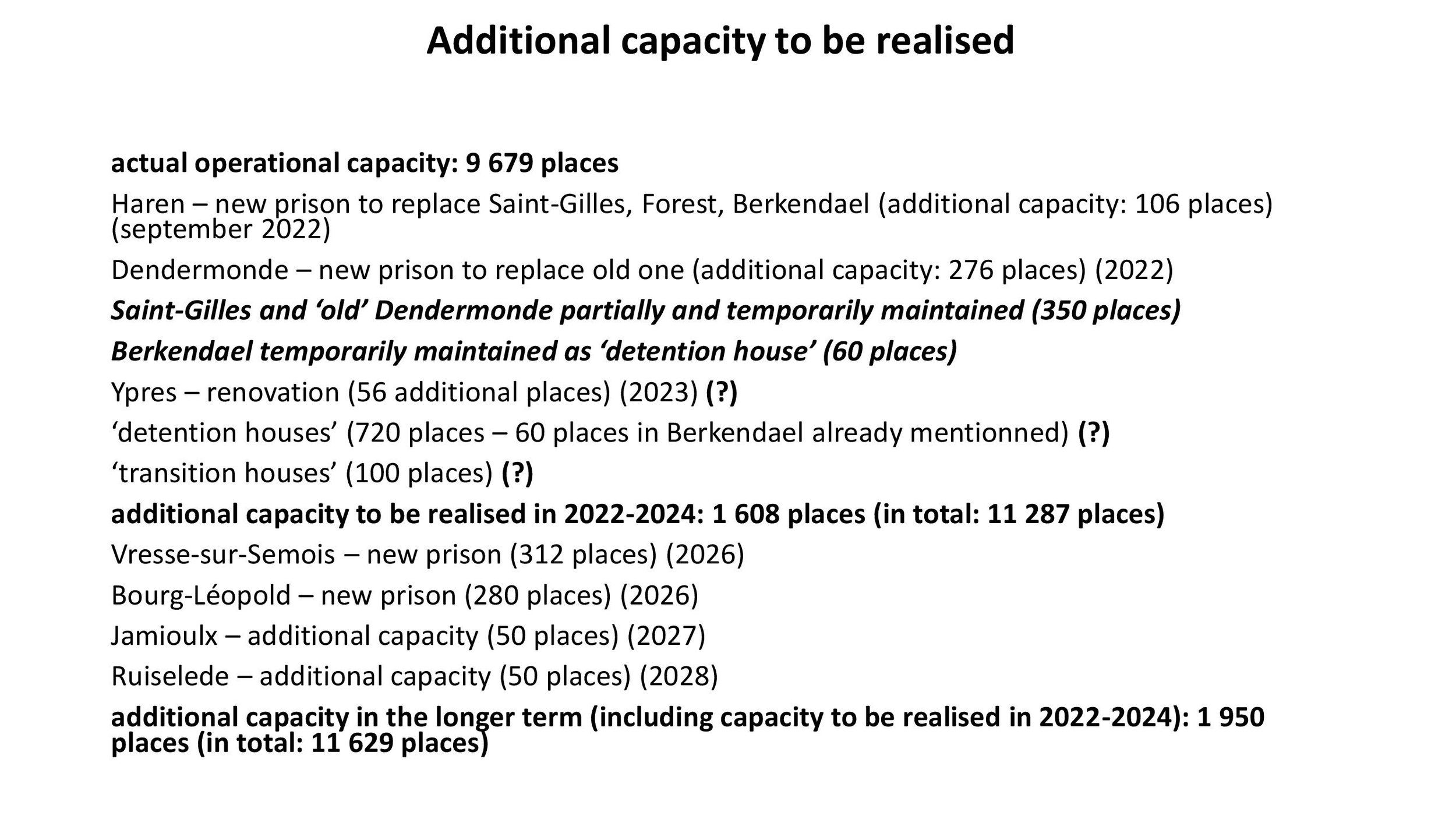
The Greek government announced the establishment of new prisons. The new prison of Drama is operational (only one wing).
A number of new staff was hired in 2023-2024.
A new domestic remedy was adopted in October 2022 [Art 6a of the Penitentiary Code].
… and what the Greek government has failed to do:
The recommendations addressed by the CPT are in most of the cases still not implemented.
The findings of the ECtHR as regards Art. 3 (overpopulation and material prison conditions) are not efficiently redressed.
The findings of the ECtHR as regards Art. 13 (domestic remedy) are not efficiently redressed.
Hellenic League for Human Rights raised the following concerns about ineffective implementation:
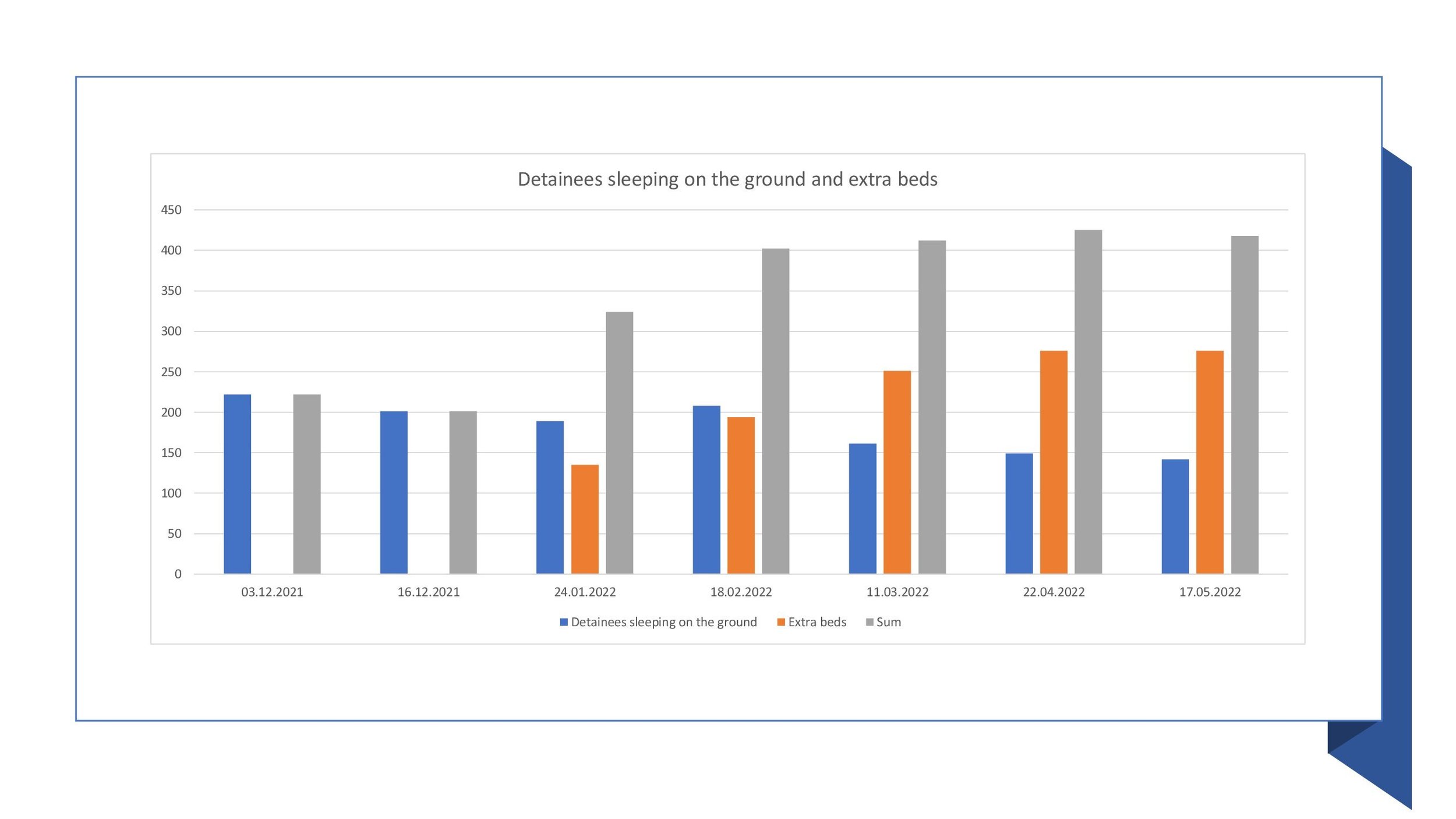
Overcrowding is still an enduring structural problem affecting a large number of detainees.
There is a high number of friendly settlements concluded between the Government and the applicants amounts to acknowledgment that prison conditions do not comply with Art. 3.
New provisions of the Criminal Code will cause serious increase of prison population.
The expected new prison establishments are not going to solve the problem of overpopulation (CPT 2022, paras. 13, 16).
No measures have been taken in order to redress inadequate transfers of prisoners by police vehicles.
No measures have been taken as regards disciplinary cells.
The domestic remedy introduced in October 2022 (Art. 6a Pen. Code) is not effectively implemented.
All 350 applications of Art. 6a have been rejected by the Court Councils. All relevant decisions were outdated.
Already, the Greek Ombudsman (2024) said that Art. 6a “is not an adequate measure to improve detention conditions when they amount to a violation of Art. 3 ECHR”.
The NGO requested the Committee of Ministers to ask the Greek authorities to:
Draft and enforce a genuine “Strategic plan” after dialogue with stakeholders setting a specific timetable, ensuring funding sources, and indicating specific sustainable measures for decongestion.
Start working with the most highly overpopulated prisons (Komotini, Korydallos, Ioannina, Volos, Nafplion, Tripoli, Chios). Implement alternative measures (social work) and expand rural prisons.
Guarantee regular allocation of funds for prisons: upgrading prison premises and staff. Not expanding closed prison places but ensuring more than 3 sq.m. of “free space to move” to each inmate.
Urgently reconsider criminal policy which has been adopted. Increasing sentences will result in extreme suffocation of the prison establishments.
Hire additional custodial trained staff and conduct regular training on security, crisis management, health issues etc, in relation to prison to all existing staff.
Reconsider implementation Art. 6A of the Penitentiary Code, as it has been proved that it can not offer guarantees as an effective means to redress prison conditions.
See slides for full briefing.
Relevant Documents
NGO Communications:
CM Decisions:
The Manole and others v the Republic of Moldova case concerns concerns undue interferences with the right of freedom of expression of journalists, editors and producers working at the state television company Teleradio-Moldova on account of censorship and political control by the state authorities in the period 2001-2006. The Court found a violation of Article 10 arising inter alia from insufficient statutory guarantees of independence for the public broadcaster. It noted that the legislative framework had been flawed throughout, in that it did not provide sufficient safeguards against the control of Teleradio-Moldova’s senior management, and thus its editorial policy, by the political organ of the government.
The Court indicated under Article 46 that the Republic of Moldova was under a legal obligation to take general measures at the earliest opportunity to remedy the situation, including by undertaking legislative reform to ensure that the legal framework complies with the requirements of Article 10, which also takes into account the Committee of Ministers' Recommendation Rec(96)10 on the guarantees of the independence of public service broadcasting and the recommendations of the Council of Europe experts on the draft law on public service broadcasting in Moldova.
Independent Journalism Centre outlined the key facts and the rights violations of the case:
General Principles (Pluralism in Audiovisual Media)
Teleradio-Moldova (TRM) held a position of dominance (private TVs were too weak).
The authorities had the duty (positive obligation) to ensure: the public access to impartial and accurate information & diversity of political outlook; journalists & other professionals are not prevented from imparting info.
Interference with the applicants' right to freedom of expression:
Media employees – directly affected by the policy applied by their employer
Sanctions taken by an employer -> interference with freedom of expression
Conclusion on compliance with Article 10:
TRM enjoyed virtual monopoly over audiovisual broadcasting in Moldova.
The State failed to comply with its positive obligation.
The legislative framework was flawed (it did not provide sufficient safeguards against the control of TRM's senior management, and thus its editorial policy, by the political organ of the Government).
These flaws were not remedied when Law on TRM (2002) was adopted.
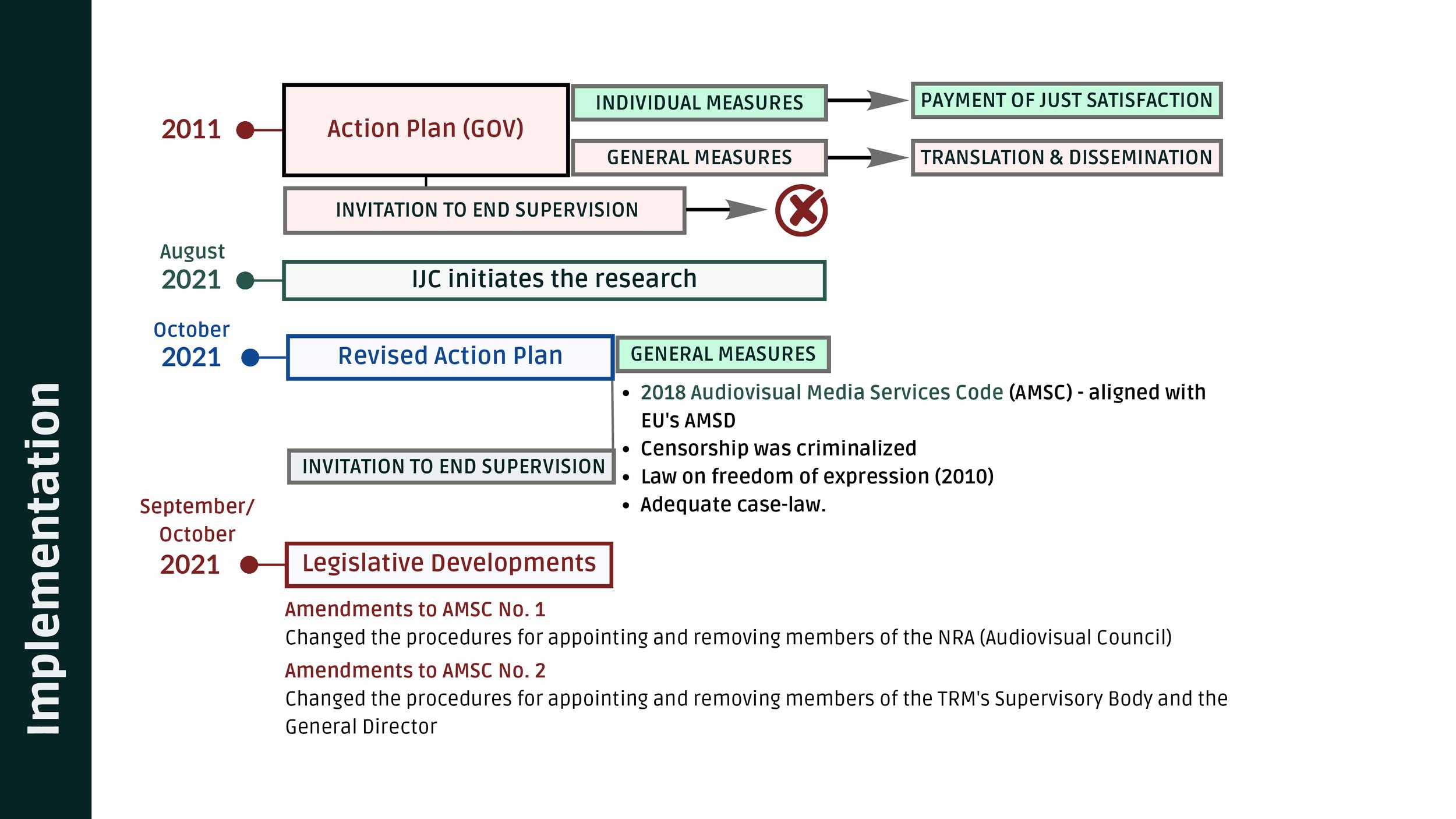
Independent Journalism Centre assessed the legislative framework in 2021:
Despite some positive preliminary findings (such as the criminalization of censorship), the law still allowed for a general tendency to favor (slightly) the Government.
Causes: Funding mechanism & indirect interference in the selection of Supervisory Body
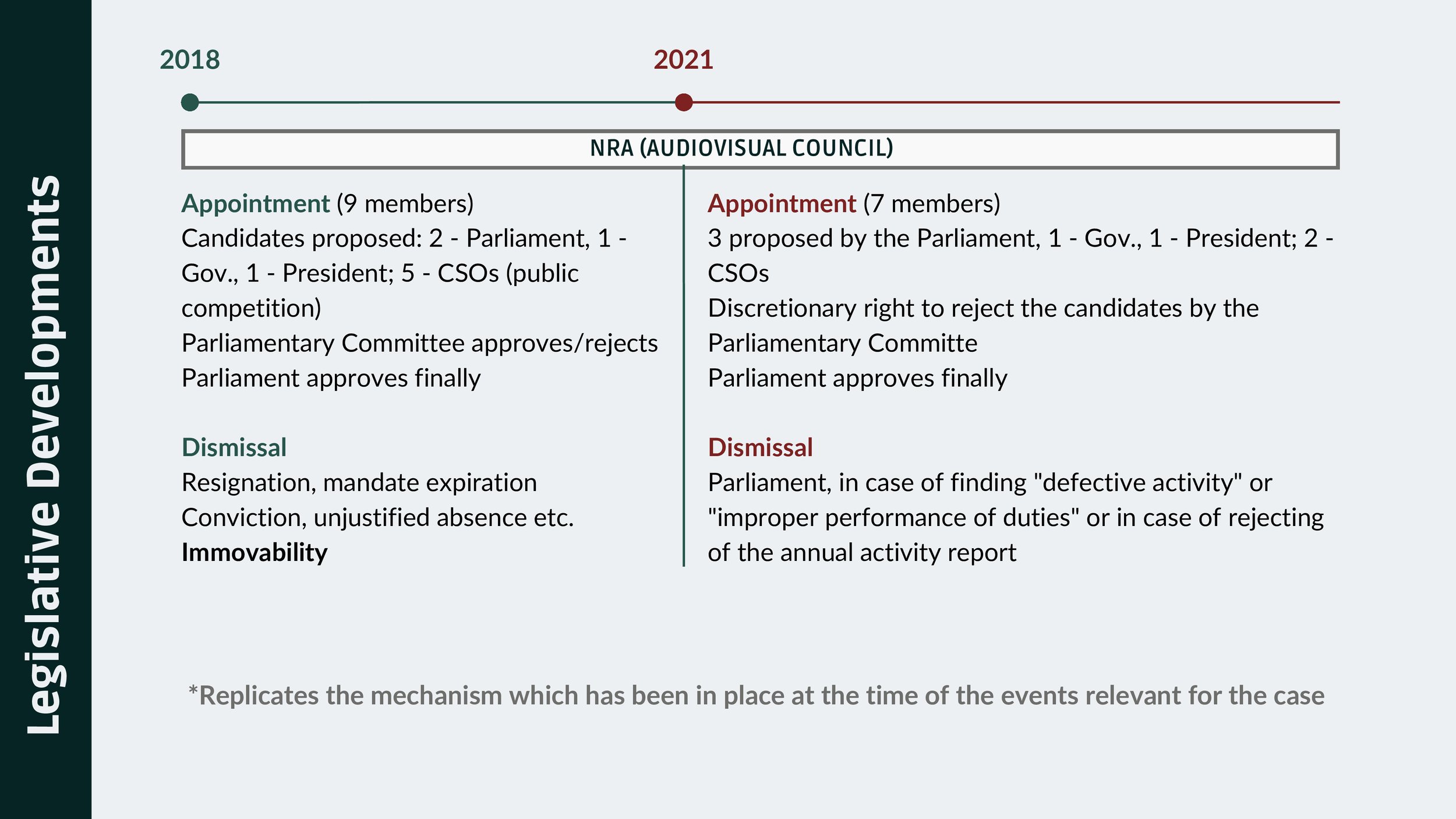
In 2021, two main amendments had been enacted to the Code of Audiovisual Media Services
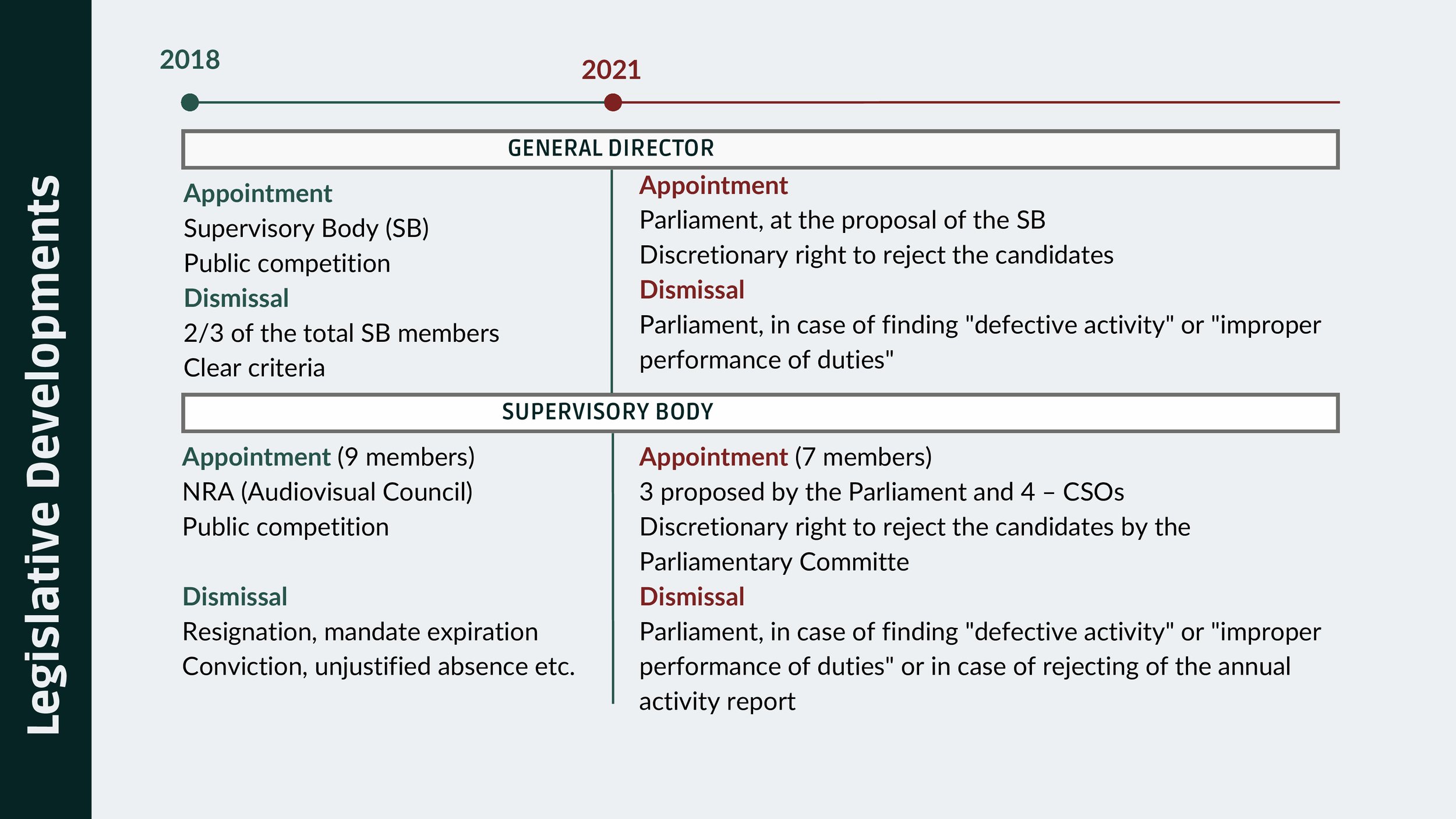
Amendments changed procedures for appointing and removing members of the NRA (Audiovisual Council), enabling its’ members to be appointed by Parliament, which also has discretionary right to reject the candidates. Furthermore, NRA (Audiovisual Council) members can be dismissed by Parliament, in case of finding "defective activity" or "improper performance of duties" or in case of rejecting of the annual activity report.
Amendments changed the procedures for appointing and removing members of the TRM's Supervisory Body and the General Director:
General Director to be appointed by Parliament at the proposal of the Supervisory Council (SC). Parliament given discretionary right to reject candidates.
Dismissal of General Director by Parliament, in case of finding “defective activity”, improper performance or non-performance of the duties.
Appointment of General Director by Parliament & CSOs. The Parliamentary Commission has the last word.
Dismissal of Supervisory Council if Parliament finds “defective activity”, improper performance or non-performance of the SC duties. Rejection of the annual activity report.
Updated Action Plan by Authorities (December 2023) and Independent Journalism Centre’s concerns:
Several general measures were presented by the authorities:
Draft Law no. 218 of 4 July 2023 amending the Code of Audiovisual Media Services and Draft Law on the Subsidy Fund.
These draft laws are unrelated to the implementation of the ECtHR judgment in the present case. The regulations do not extend their purview to encompass the public broadcaster or NRA.
The commitment of the Parliamentary Committee (PC) regarding the review of the relevant provisions of the Code of Audiovisual Media Services so as to secure the independence of the members of the Supervisory Council of TRM:
Independent Journalism Centre is a member of the Parliamentary Joint Working Group
The matter pertaining to the review of relevant provisions within the AMSC has not been deliberated within the agenda of the PC/PJWF
Requests made by the IJC to instigate efforts in this regard have yet to be acknowledged or acted upon
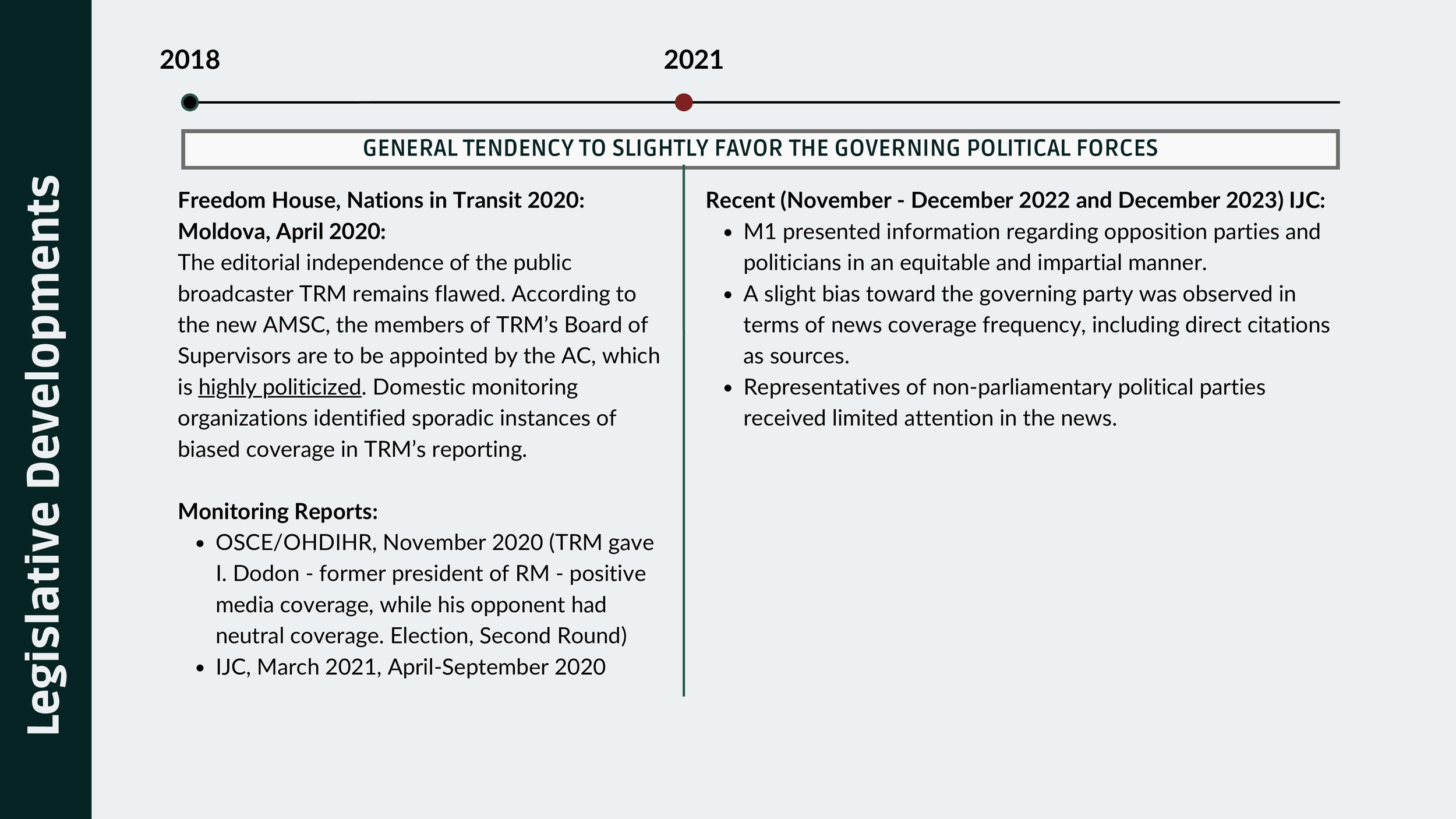
Independent Journalism Centre highlights the evidence on the general tendency to favor governing political forces:
Freedom House, Nations in Transit 2020: Moldova, April 2020: “The editorial independence of the public broadcaster TRM remains flawed. According to the new Code of Audiovisual Media Services, the members of TRM’s Board of Supervisors are to be appointed by the AC, which is highly politicized. Domestic monitoring organizations identified sporadic instances of biased coverage in TRM’s reporting.”
Monitoring Reports: OSCE/OHDIHR, November 2020 (TRM gave I. Dodon - former president of the Republic of Moldova - positive media coverage, while his opponent had neutral coverage. Election, Second Round); IJC, March 2021, April-September 2020
Recent (November - December 2022 and December 2023): a slight bias toward the governing party was observed in terms of news coverage frequency, including direct citations as sources; representatives of non-parliamentary political parties received limited attention in the news.
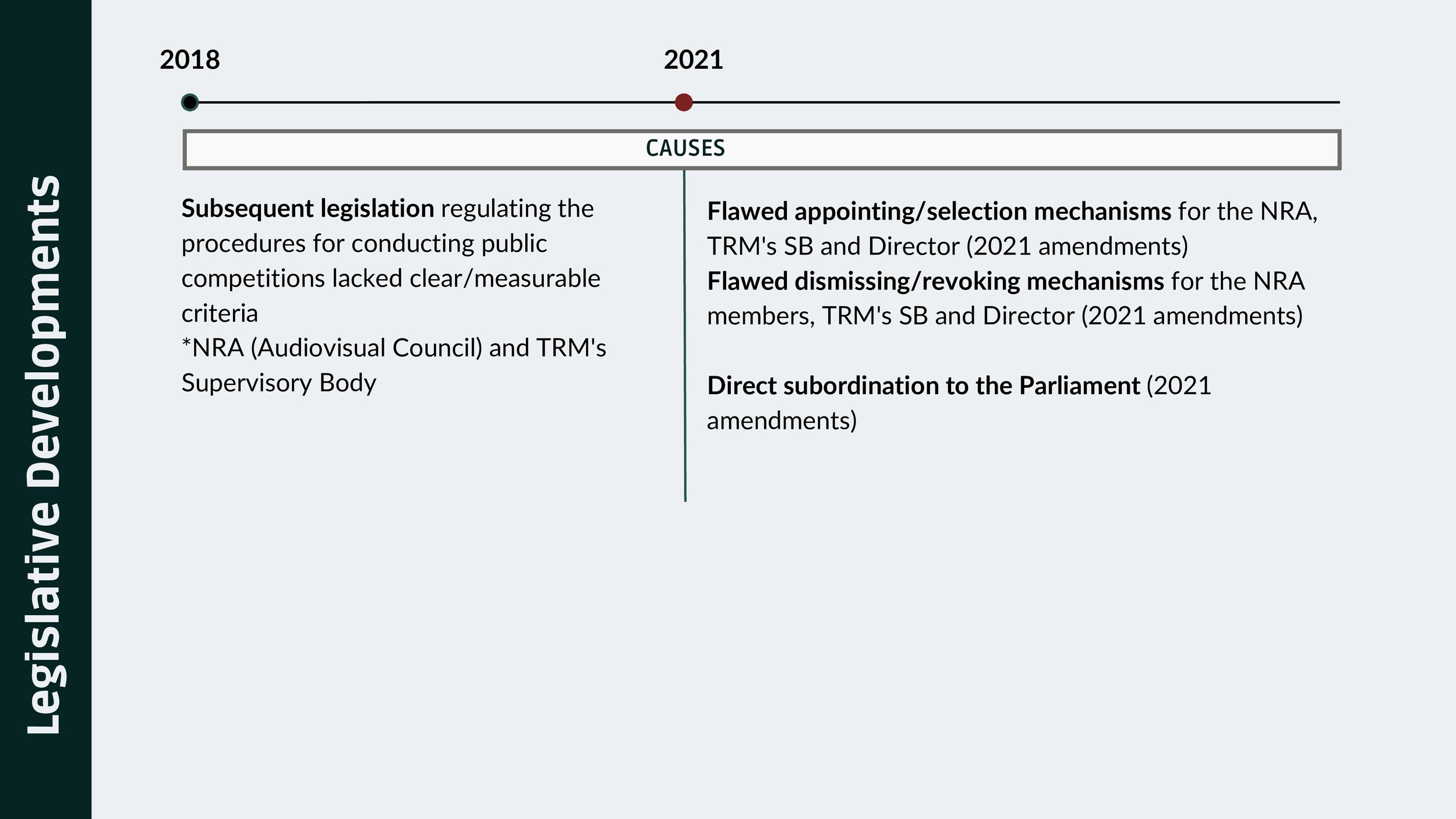
The 2021 legislative amendments are characterized by:
Flawed appointing/selection mechanisms for the NRA (Audiovisual Council), TRM's Supervisory Body and General Director
Flawed dismissing/revoking mechanisms for the NRA (Audiovisual Council) members, TRM's Supervisory Body and General Director
Direct subordination to the Parliament.
The Independent Journalism Centre asked the Committee to request Moldovan authorities to:
Review the pertinent provisions of the Audiovisual Media Services Code No. 174/2018;
Reinstate the mechanisms that govern the status and composition of the NRA (Audiovisual Council), TRM's Supervisory Body, and senior management, as outlined in the 2018 version of the Audiovisual Media Services Code;
Ensure that these mechanisms include clear safeguards for a genuine independence of the NRA and immovability of its members, as well as exclude possible political control of TRM;
Ensure that subsequent legislation overseeing the procedures for public competitions in the selection of NRA (Audiovisual Council) members, TRM's Supervisory Body, and senior management incorporates well-defined and measurable criteria for evaluating and assessing candidates;
Amend the Audiovisual Media Services Code in order to ensure that the funding model for the public broadcaster will reduce the vulnerability of TRM to influence from governing political parties.
See slides for full briefing.
Relevant Documents:
NGO Communications
CM Decisions
Darboe and Camara v Italy
The Darboe and Camara v Italy concerns the applicants placement in an adult migrant centre and the age-assessment procedure that ensued. In June 2016, the applicant, a Gambian national, arrived in Italy on makeshift vessels, and claimed asylum as unaccompanied minor. No information on how to initiate the relevant procedure had been provided to him and no request for international protection had been lodged in his case. After an initial placement in a centre for foreign unaccompanied minors he was transferred to an adult reception, overcrowded and lacking adequate facilities and healthcare, where a medical examination (wrist X-ray examination) concluded that he was an adult of eighteen years old. His stay in the adult reception centre lasted more than four months.
ASGI outline the key facts of the case & the Government’s recent Action Report to participants:
Unaccompanied minor placed in an adult reception center: overcrowded, lacking adequate facilities and healthcare, for more than 4 months. No guardian appointed, no information and access to asylum procedure.
Identified as adult based on wrist X-ray examination, without procedural safeguards.
Violations of:
Article 8: lack of procedural guarantees in age assessment procedure > no access to rights as unaccompanied minor.
Article 3: conditions and duration of stay in adult reception center.
Article 13 with 3 and 8: lack of remedy to complain about reception conditions and age assessment.
Government’s Action Report 2023 and communication January 2024 presented general measures:
Law 47/17 on unaccompanied minors (UAMs)
Increase of reception system’s capacity
National Plan against Human Trafficking
Law Decree 133/23 conv. Law 176/23 in response to emergency increase in migrants’ arrivals
Request for closure of the supervision.
ASGI highlights their concerns regarding General Measures:
Measures implemented do not prevent recurrence of systemic violations of Articles 3, 8 and 13, similar to Darboe and Camara case:
Limited implementation of Law 47/17 in practice
Law Decree 133/23 conv. Law 176/23 seriously worsened the legal framework regarding UAMs reception and age assessment > rights violations likely to increase.
Concerns about practices and new legislation have been expressed by the National Ombudsperson for the Rights of the Child, the Association of Juvenile Judges, UNICEF, Save the Children
Reception Conditions
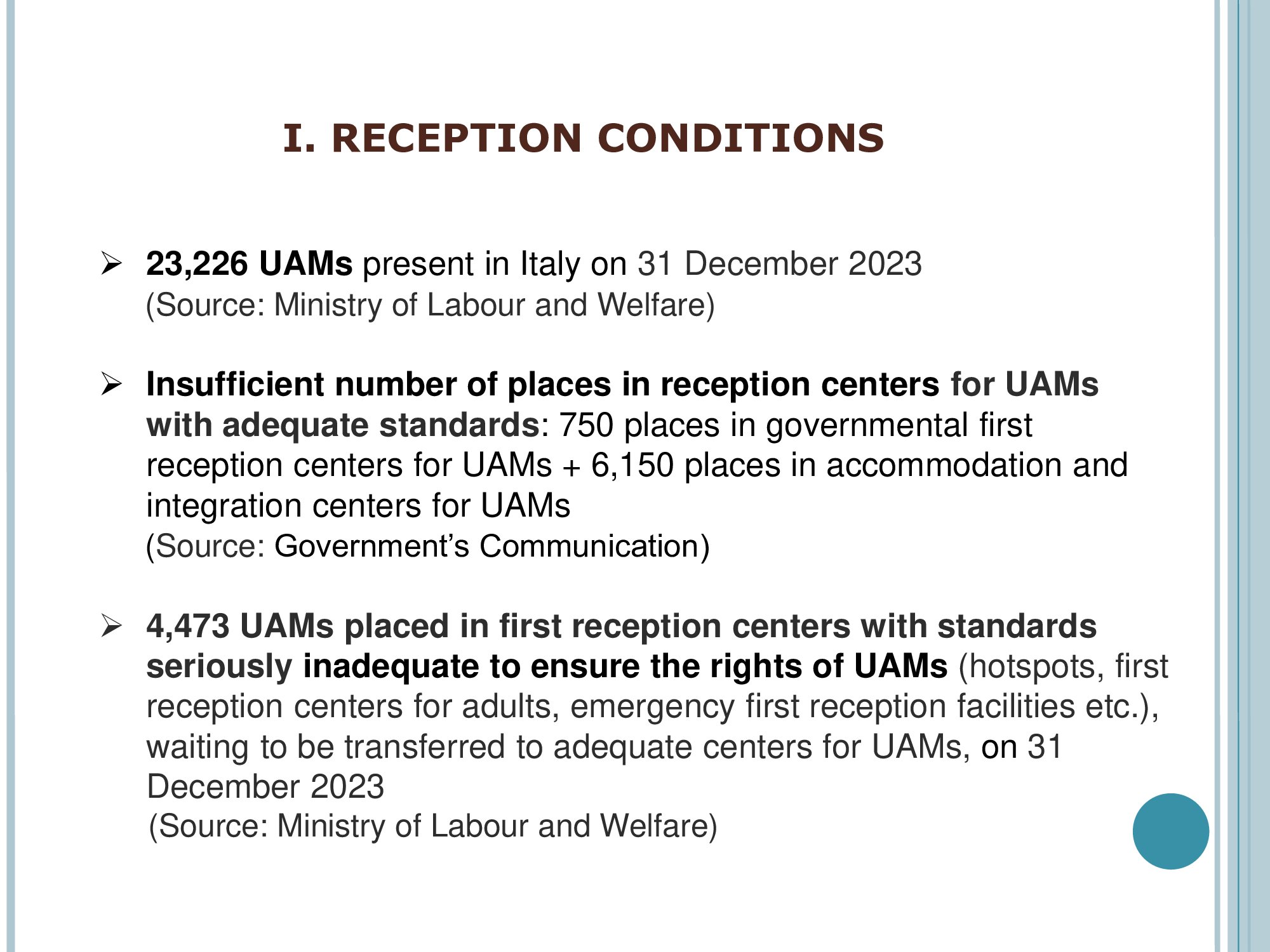
23,226 UAMs present in Italy on 31 December 2023 (Source: Ministry of Labour and Welfare)
Insufficient number of places in reception centers for UAMs with adequate standards: 750 places in governmental first reception centers for UAMs + 6,150 places in accommodation and integration centers for UAMs (Source: Government’s Communication).
4,473 UAMs placed in first reception centers with standards seriously inadequate to ensure the rights of UAMs (hotspots, first reception centers for adults, emergency first reception facilities etc.), waiting to be transferred to adequate centers for UAMs, on 31 December 2023 (Source: Ministry of Labour and Welfare)
Law Decree 133/23 has introduced the possibility to place UAMs aged 16+ in adult reception centers:
pending the transfer to centers for UAMs, for up to 5 months
in dedicated sections, but no indications to avoid promiscuity with adults
no specialized staff and services for UAMs provided
The placement of UAMs in adult reception centers, that happened in practice but was forbidden by law until October 2023, is likely to increase
Widespread and increasing detention of UAMs in adult reception centers in inadequate conditions
with no legal basis and procedural guarantees (detention of UAMs forbidden by D.Lgs. 142/15, Art. 19, para. 4)
Hotspots and governmental reception centers in Lampedusa, Pozzallo/Cifali, Taranto, Crotone, Restinco
In the adult reception centers and emergency first reception facilities monitored by ASGI, UAMs were in conditions similar to Darboe and Camara case:
inadequate material conditions, in some cases overcrowding and promiscuity with adults
no guardian appointed, no access to asylum procedure and legal support
no or limited access to health care, psychological assistance and education
lasting several months
serious stress in the children, exacerbated by deprivation of liberty
No remedy to complain about reception conditions has been introduced
Placement in inadequate reception centers also hinders identification of UAMs victims of trafficking > prevents implementation of National Plan against Human Trafficking
Three Rule 39 applications to ECtHR (October-December 2023):
UAM detained in adult reception center in Crotone for 5 months
UAM detained in adult reception center in Restinco for 2 months
UAM detained in a Police station in Rome for 6 days
In the three cases ECtHR decided interim measures: transfer to adequate reception center for UAMs
Increased influx of UAMs does not exonerate Italy from the respect of international human rights, and in any case no derogation from obligations under Article 3 is admissible
Age Assessment Procedure
Limited implementation of procedural safeguards established by Law 47/17: e.g. multidisciplinary teams have not been established in many areas
Law Decree 133/23 conv. Law 176/23 introduced an age assessment procedure derogating from most procedural safeguards established by Law 47/17:
no appointment of a guardian, access to a lawyer and informed participation
medical examination, no multidisciplinary approach
no judicial decision on age assessment
5 days to lodge an appeal, without automatic suspension of proceedings resulting from identification as an adult
no access to an effective remedy and not consistent with the principle of presumption of minor age
ASGI provided their Recommendation to the Committee of Ministers and for Italian Authorities:
Considering the persisting and increasing systemic violations of Articles 3, 8 and 13, the Committee of Ministers should continue the monitoring procedure under enhanced supervision and all upon Italian authorities to:
Amend Law 176/23 provisions regarding the reception of UAMs in adult centers and the age assessment procedure derogating from the safeguards established by Law 47/17
Cease unlawful de facto detention of UAMs
Increase the capacity of adequate reception system for UAMs
Ensure that procedural safeguards in age assessment procedures established by Law 47/17 are respected in practice.
See slides for full briefing.
Relevant Documents:
NGO Communications
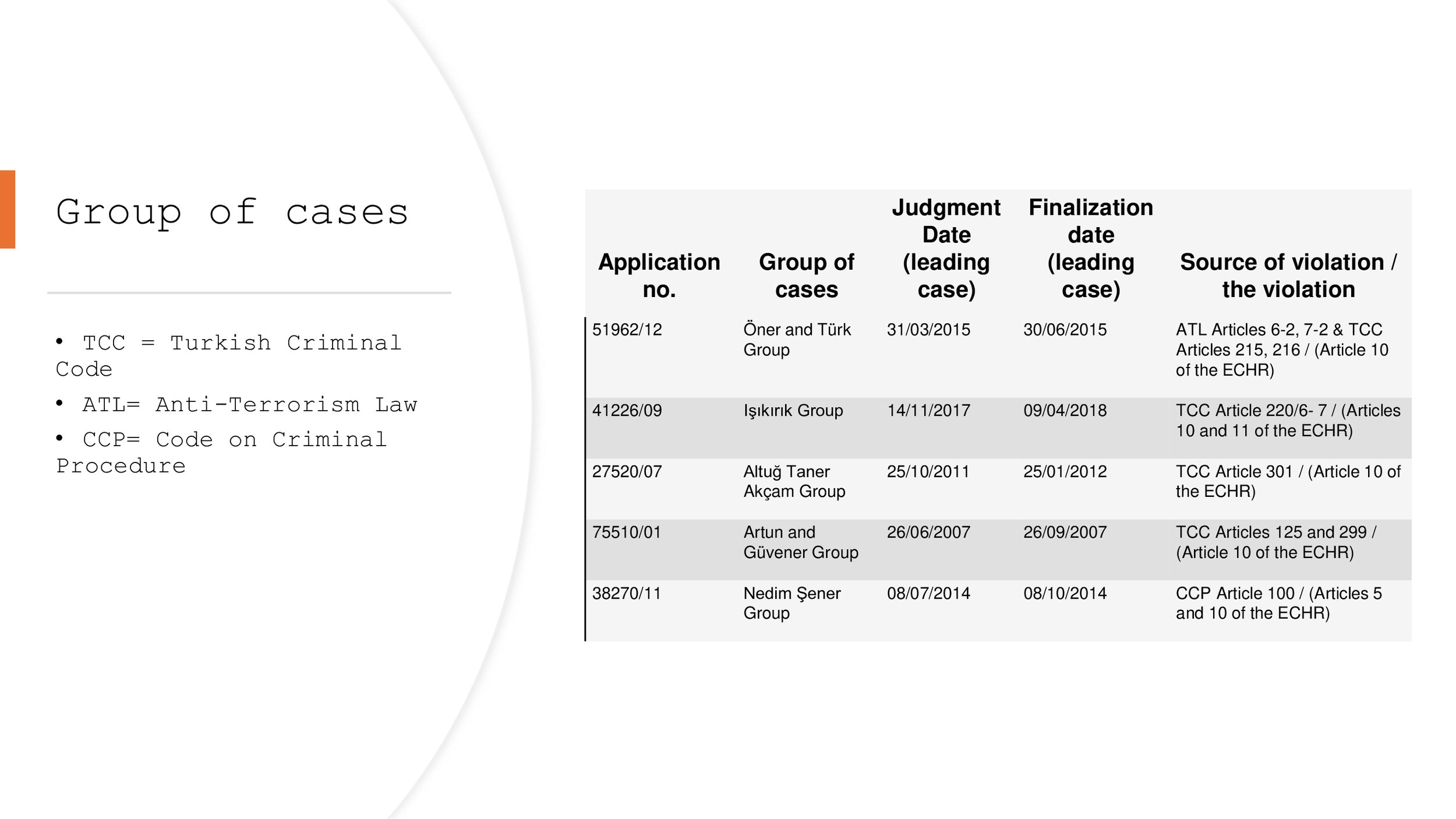
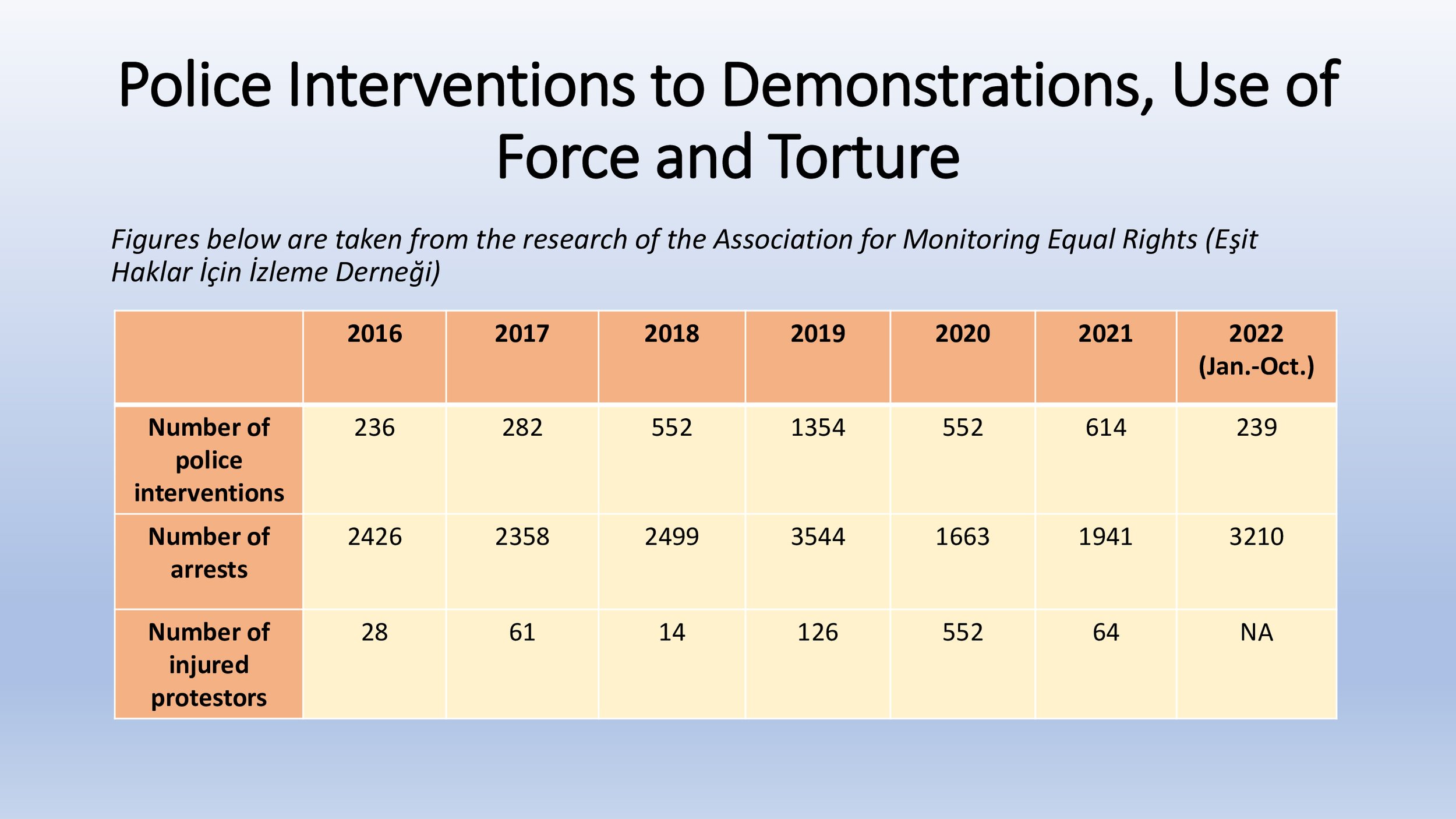
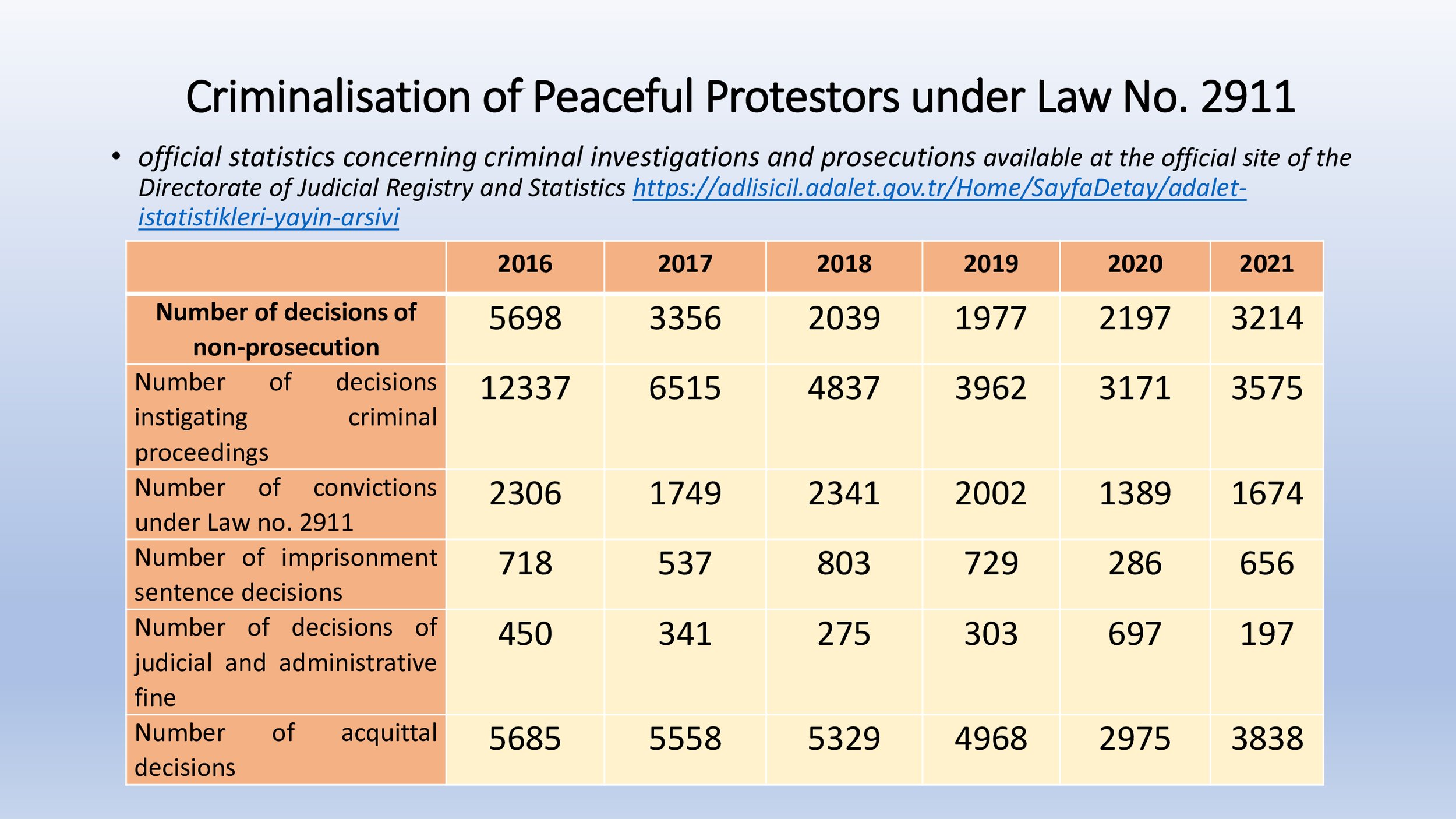
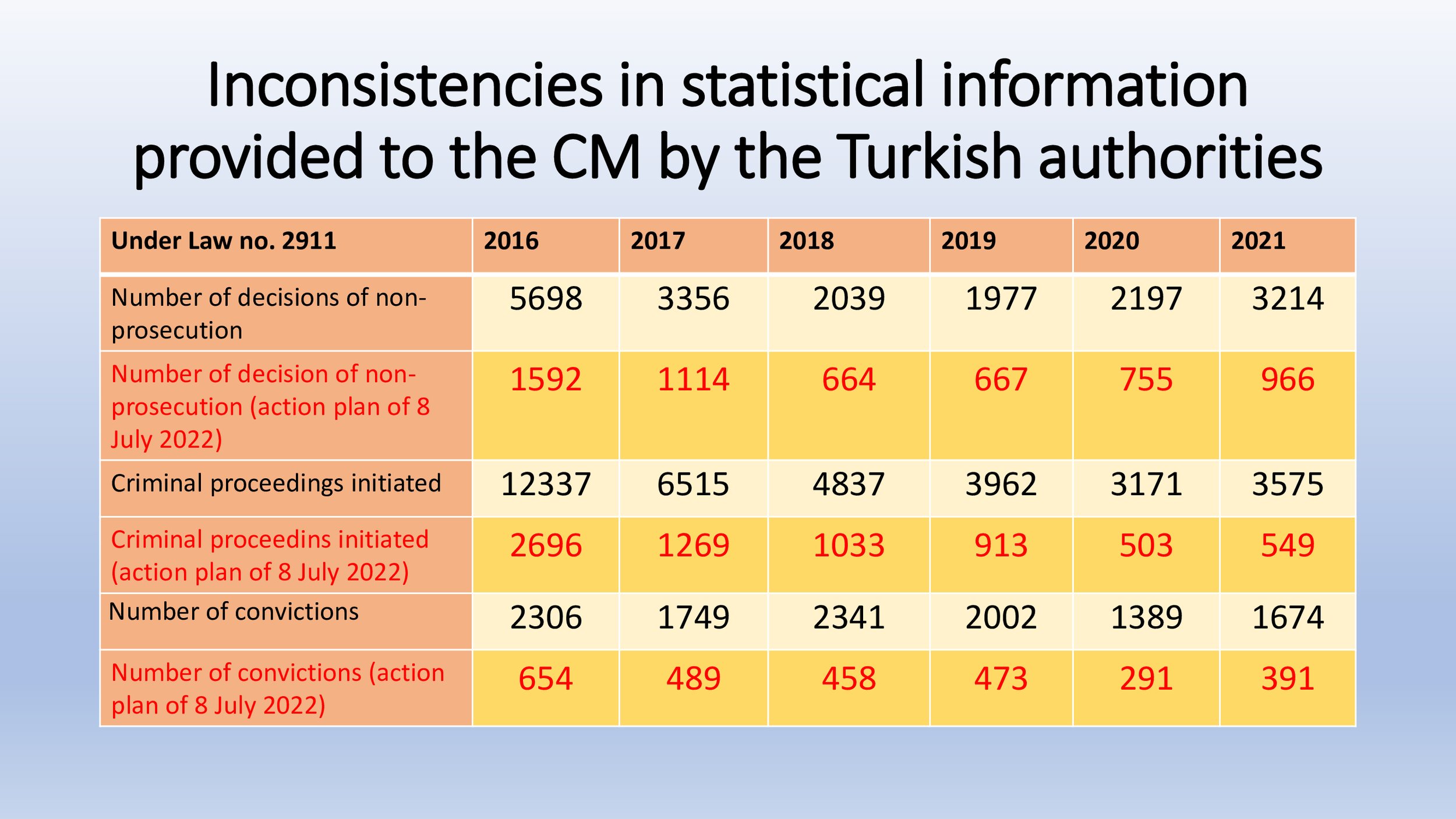
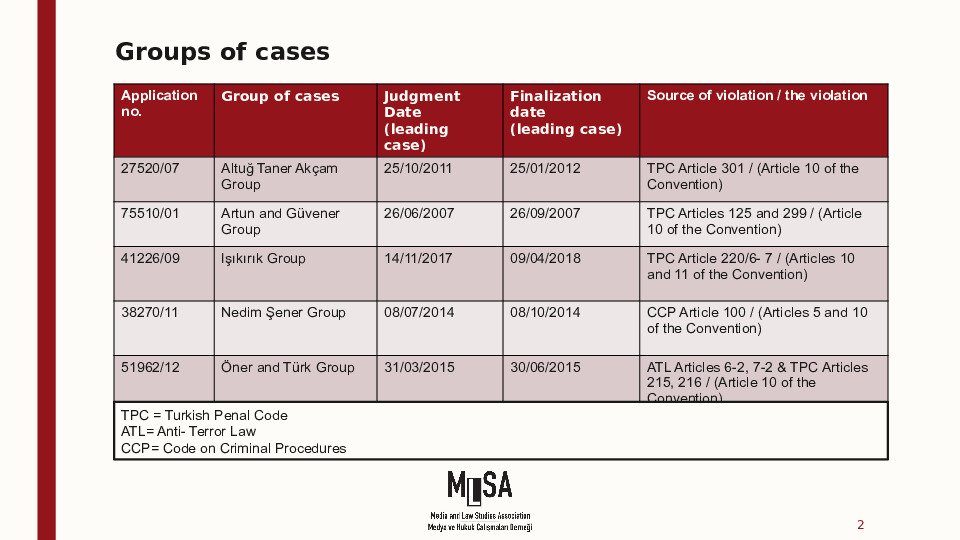
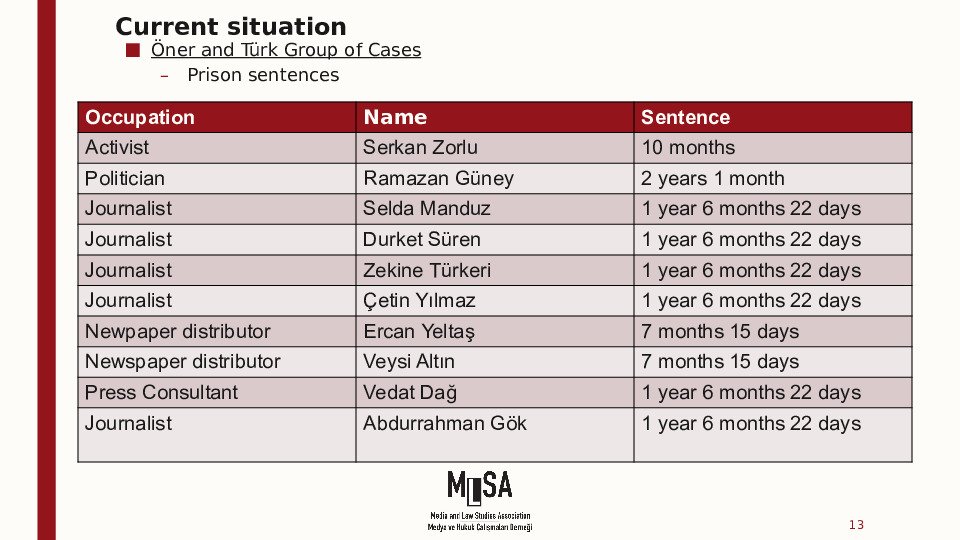
The Öner and Turk v Türkiye, Işıkırık v Türkiye, Altuğ Taner Akçam v Türkiye, Artun and Güvener v Türkiye and Nedim Şener v Türkiye groups of cases concern unjustified and disproportionate interferences with the applicants’ freedom of expression on account of criminal proceedings for having expressed opinions that did not incite hatred or violence, and the consequent chilling effect on society as a whole.
Hafiza Merkezi outlined the subject matter of the five groups and provided information on the legislative status of relevant provisions:
Öner and Türk group of cases
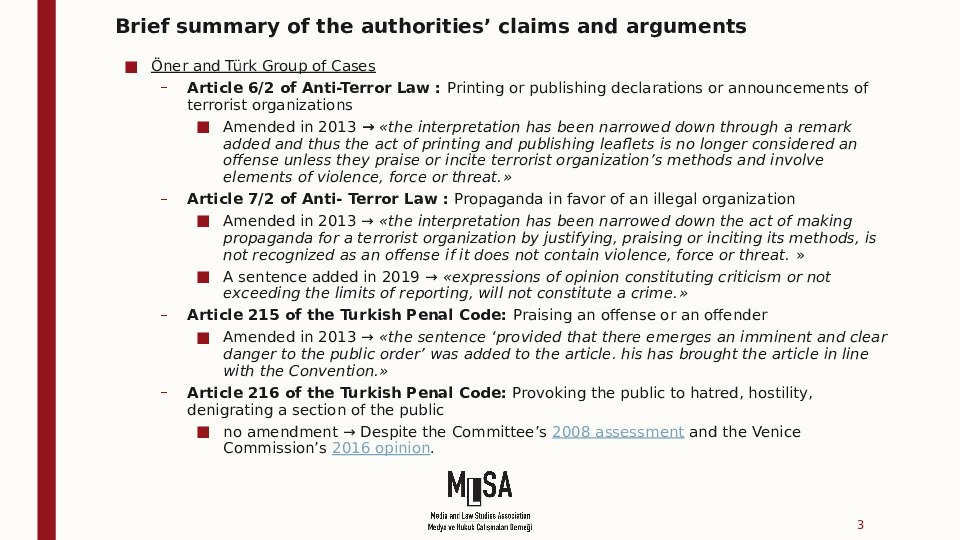
The Öner and Türk group concerns the unjustified conviction of the applicants for offences under the Anti-Terrorism Law (ATL) (mainly Article 6 § 2 - printing of statements made by a terrorist organisation - and Article 7 § 2 - propaganda in favour of an illegal organisation) or Articles 215 or 216 of the Criminal Code (praising an offence or an offender, or provoking the public to hatred, hostility, denigrating a section of the public on grounds of social class, race, religion, sect, gender or regional differences).
Article 6 § 2 of ATL- printing of statements made by a terrorist organization
Amendment added in 2013: “condoning, praising or encouraging methods [using] coercion, violence or threats”
Article 7 § 2 of ATL - propaganda in favour of an illegal organisation
Amendment added in 2013: “by justifying, praising or encouraging the use of methods constituting coercion, violence or threats”
Amendment added in 2019: “Expressions of thought that do not exceed the limits of reporting or for the purpose of criticism shall not constitute a crime”
No new amendment, continuing violations
Article 215 of CC - praising an offence or an offender
Amendment added in 2013: “…provided that there emerges an imminent and clear danger to the public order”
No new information provided
Article 216 of CC - provoking the public to hatred, hostility, denigrating a section of the public on grounds of social class, race, religion, sect, gender or regional differences
No amendment
No information provided in the action plan
Article 6 § 1 of ATL - disclosing or publishing the identities of officials on counter-terrorism duties, or identifying such persons as targets
Ambiguous wording, increasing use against journalists and rights defenders
Previously examined before the ECtHR and the CM
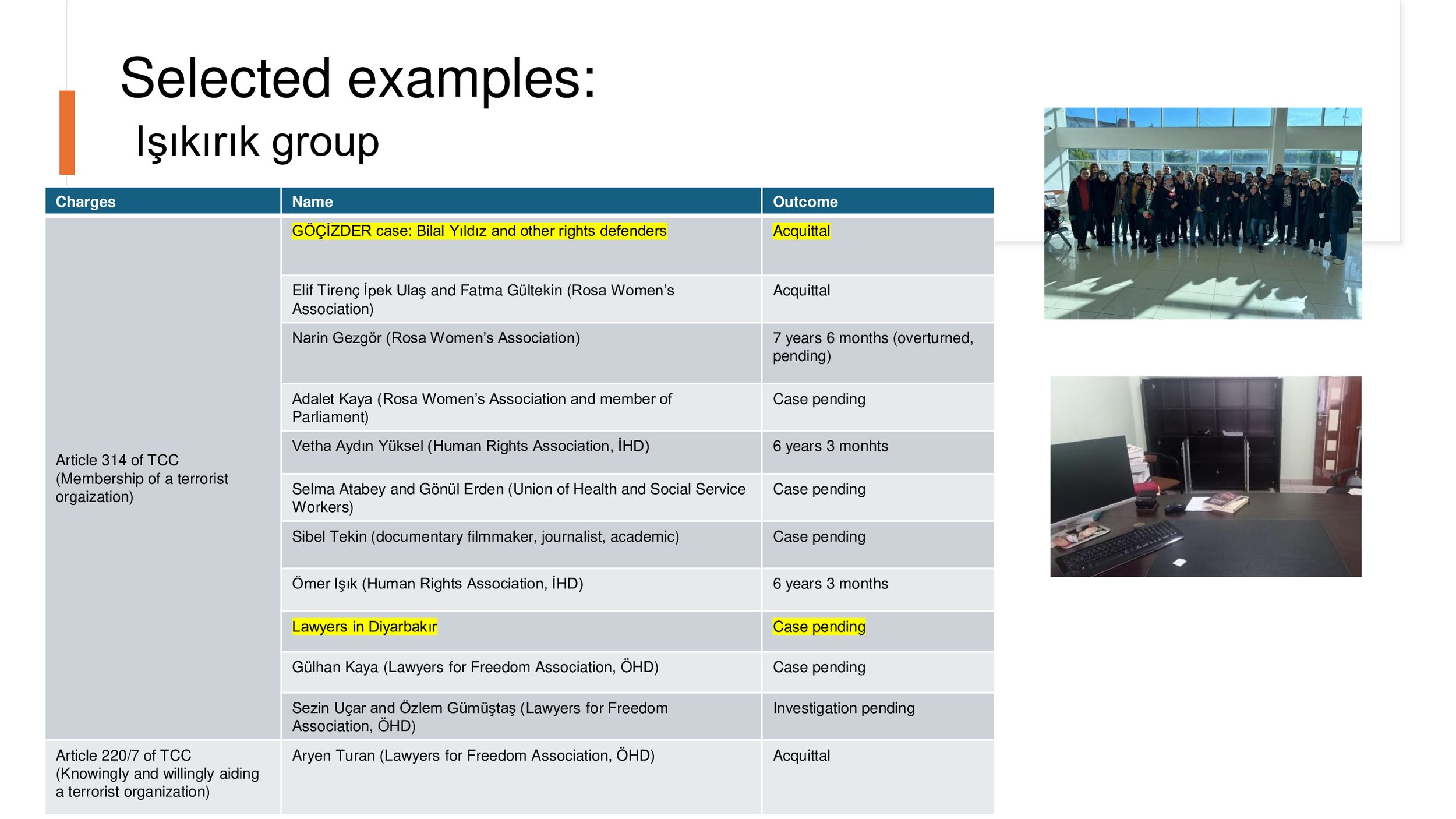
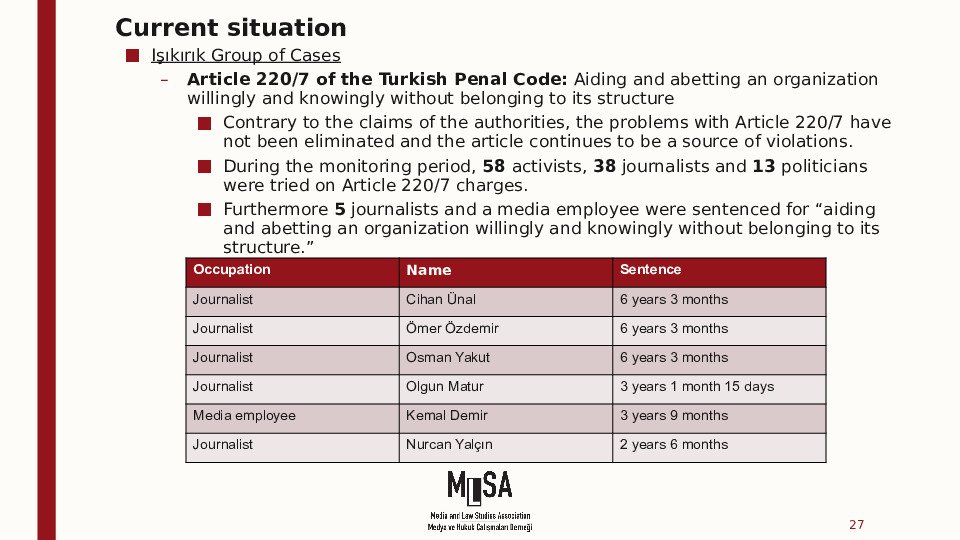
Işıkırık group of cases
The Işıkırık group concerns Article 220 §§ 6 and 7 of the Criminal Code, which provide that anyone who commits a crime on behalf of an illegal organisation or who knowingly and willingly aids and abets an illegal organisation shall be sentenced as a member of that organisation. Based on these provisions, most of the applicants in this group of cases were sentenced to several years of imprisonment for membership of an illegal organisation for having, for example, peacefully participated in a demonstration called for by an illegal organisation, or expressed a positive opinion about such an organisation, without the prosecution having to prove the elements of actual membership.
Article 220 § 6 of the CC - committing an offense on behalf of an organization without being a member
Hamit Yakut pilot judgment of the Constitutional Court (2021) – not implemented by the Parliament
Annulment by the Constitutional Court (2023) – comes into force on 8 April 2024
Legislative proposal (currently before Parliament) offers no change.
Article 220 § 7 of the CC - aiding and abetting an organization willingly and knowingly without belonging to its structure
Amendment added in 2013: “by justifying, praising or encouraging the use of methods constituting coercion, violence or threats”
The Constitutional Court found it meets the legality requirement
No new amendment foreseen.
Altuğ Taner Akçam group of cases
The Altuğ Taner Akçam group deals with prosecutions under Article 301 of the Criminal Code (publicly denigrating the Turkish nation or the organs and institutions of the state, including the judiciary and the army), which the Court found not to meet the “quality of law” requirement in view of its “unacceptably broad terms”.
Article 301 of the CC - publicly denigrating the Turkish nation or the organs and institutions of the state, including the judiciary and the army
Amended in 2008: denigrating “Turkish nation” instead of “Turkishness”, lower sentences + authorization from Ministry of Justice required for investigation
The ECtHR found the provision does not meet the “quality of law” requirement since “its unacceptably broad terms result in a lack of foreseeability as to its effects” (Altuğ Taner Akçam v. Turkey, § 95)
Despite calls from the CM, no new amendment since the Taner Akçam judgment
Artun and Güvener group of cases
The Artun and Güvener group concerns criminal convictions for insulting public institutions, officials and the President under Articles 125 and 299 of the Criminal Code (the President, the Republic, police officers, tax inspectors etc.). The Court included indications under Article 46 that the violation stemmed from a problem with the drafting and application of Article 299 which afforded the Head of State privileged status or special protection vis-à-vis the right to convey information and opinions concerning him, and held that bringing the relevant domestic law into line with Article 10 would constitute an appropriate form of redress making it possible to put an end to the violation.
Article 125 of the CC – insulting
No new amendment
Article 299 of the CC – insulting the President
No new amendment
Action plan argues that “no abolishment is required” and Ministry of Justice authorization required for prosecution functions as a filtering mechanism
latest CM decision calling for the abrogation of Article 299
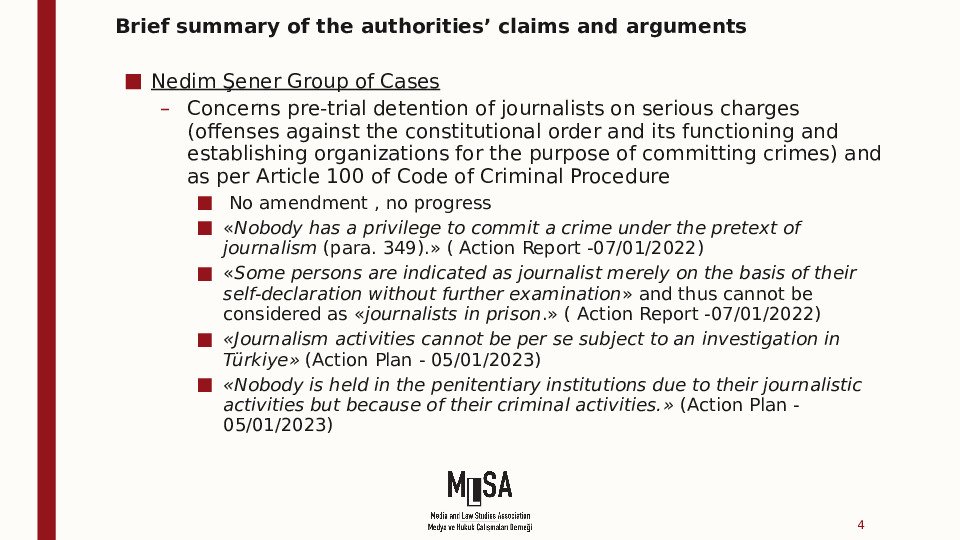
Nedim Şener group of cases
The Nedim Şener group focuses on the pre-trial detention of individuals, mainly journalists, without relevant and sufficient reasons, on serious charges based on their publications or speech. In one case in the grouo, the Court found inter alia that the applicant’s pre-trial detention was unlawful, since the offence with which he was charged, namely the dissemination of propaganda in favour of an illegal terrorist organisation, had - wrongly - been considered one of the offences listed in Article 100 of the Code of Criminal Procedure for which the reasons justifying the detention were established by legal presumption.
Article 100 of the Code on Criminal Procedure (Grounds for arrest)
Pre-trial detention used as a punitive measure and no concrete evidence sought
Lower courts even find Article 100 insufficient
CM called for the judiciary to “rely on concrete evidence justifying strong suspicion when placing individuals in detention”.
The NGO set out their main concerns regarding the implementation of these cases:
“Expressions of thought that do not exceed the limits of reporting or for the purpose of criticism shall not constitute a crime” - similar phrases added over the years had no positive impact.
Broad wording of provisions and arbitrary conduct of the judiciary.
Troubling approach associating any dissenting opinion with terrorism.
Circumventing provisions
Non-implementation of Constitutional Court judgments
Individual applications
Annulment decisions – Parliament is reluctant to make required legislative changes in a Convention compliant manner
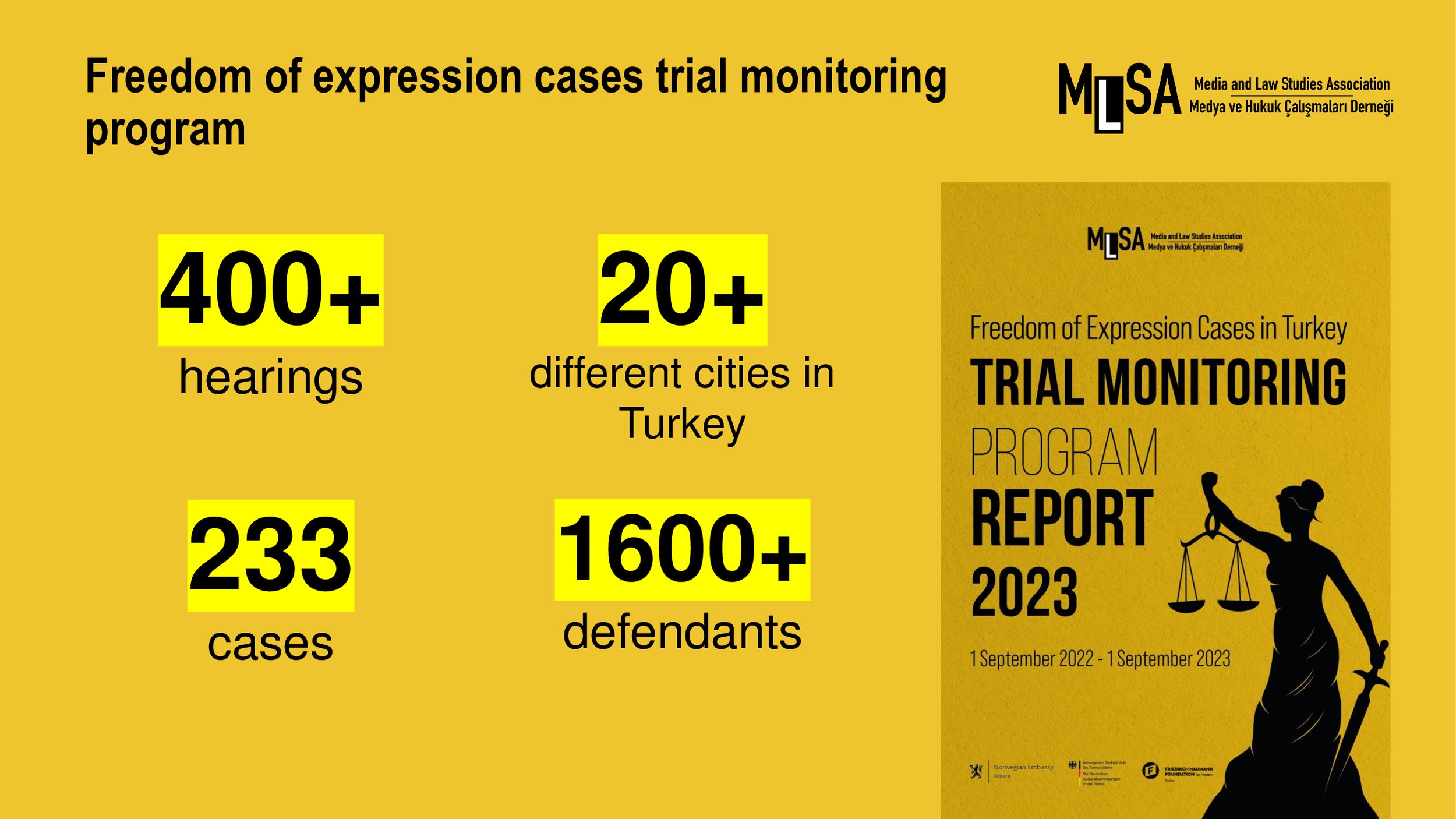
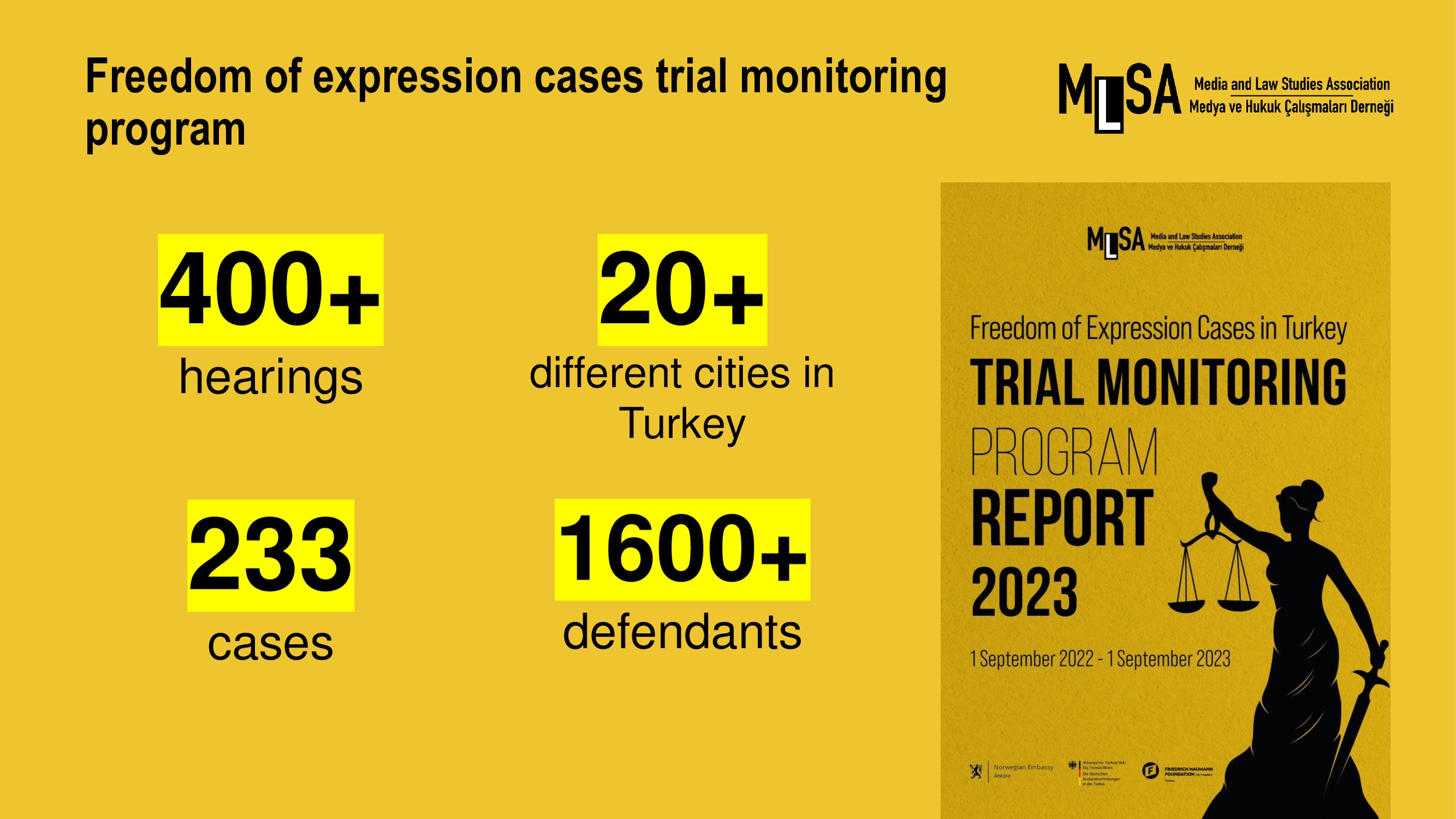
MLSA presented the findings in their 2023 Trial Monitoring Report 2023:
Öner and Türk v. Türkiye: Terrorism charges are still the primary charge against freedom of expression in Türkiye.
Terror charges are the most frequent charge in freedom of expression cases by making up for almost half of all the charges - 103 cases.
Terrorist propaganda (Anti Terror Law – 7§2) is the second crime most often prosecuted in the report – 46 cases (%15).
The government introduced amendments in 2019 to the article but courts are still failing to differentiate between terrorist propaganda and news content.
Terrorist organisation membership (7§1) are the main charge in 10% of all cases.
Targeting the individuals involved in counterterrorism (Anti Terrorism Law – 6§1) is being used to circumvent the other provisions reviewed by the committee. It was charged 12 times in last period.
Terrorist organization membership (Anti Terrorism Law – 7§1) is being used to circumvent the other provisions reviewed by the Committee.
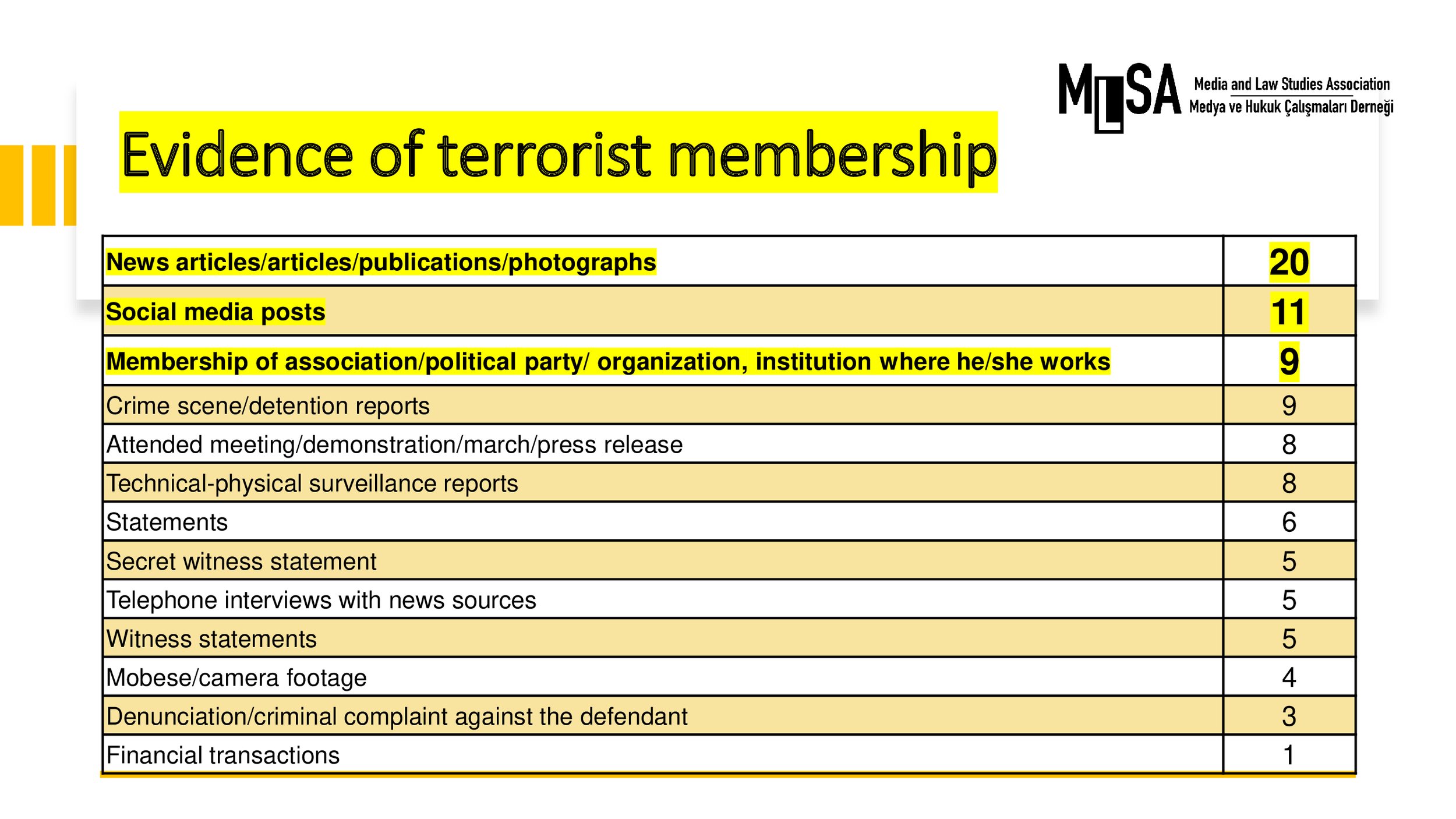
Evidence used in connection to these charges are mostly composed of news articles and social media posts.
It was used in almost 10 % of all freedom of expression cases.
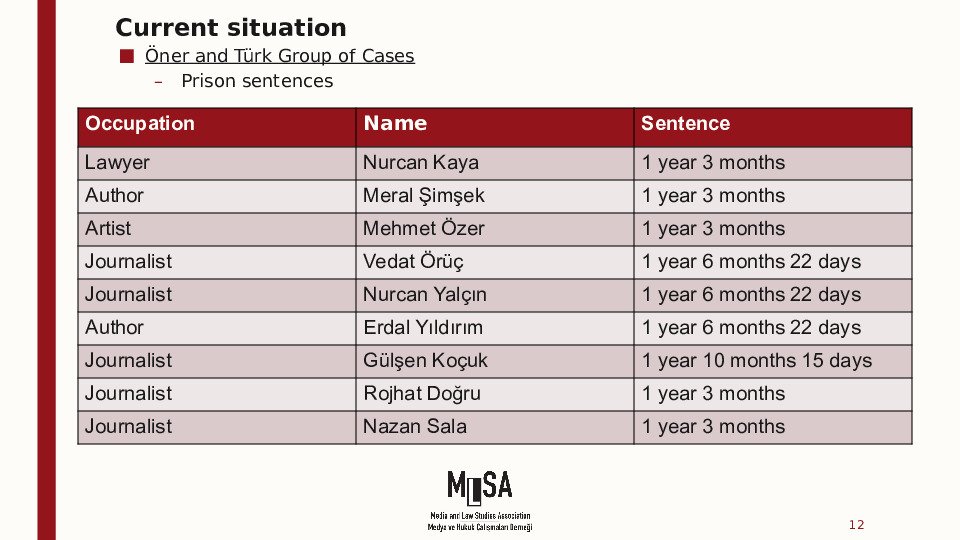
In total, in 3 cases, 5 defendants were sentenced to 31 years, 3 months and 9 days in total.
Işıkırık v. Türkiye: Annulled Article 220/6 of TPC is being reinstated and circumvented by Article 220/7.
Article 220/6 of TPC: committing a crime on behalf of a criminal organization without being a member
In one case, four journalists were sentenced to 11 years due to this charge
Article 220/7 of TPC: willingly aiding a criminal organization
In two freedom of expression cases, 32 defendants were sentenced to almost 103 years imprisonment on this charge.
Nedim Şener v. Türkiye: Detention is used as a punishment mechanism in freedom of expression cases.
Number of detained journalists is misleading without context
Compared to last year the detained defendants increased by 150%
Journalist Dicle Müftüoğlu was imprisoned since April 2023 until February 2024 without her lawyer being allowed to make a defense statement in the first hearing. Her case was only composed of her journalistic activities. No evidence was produced during her detention.
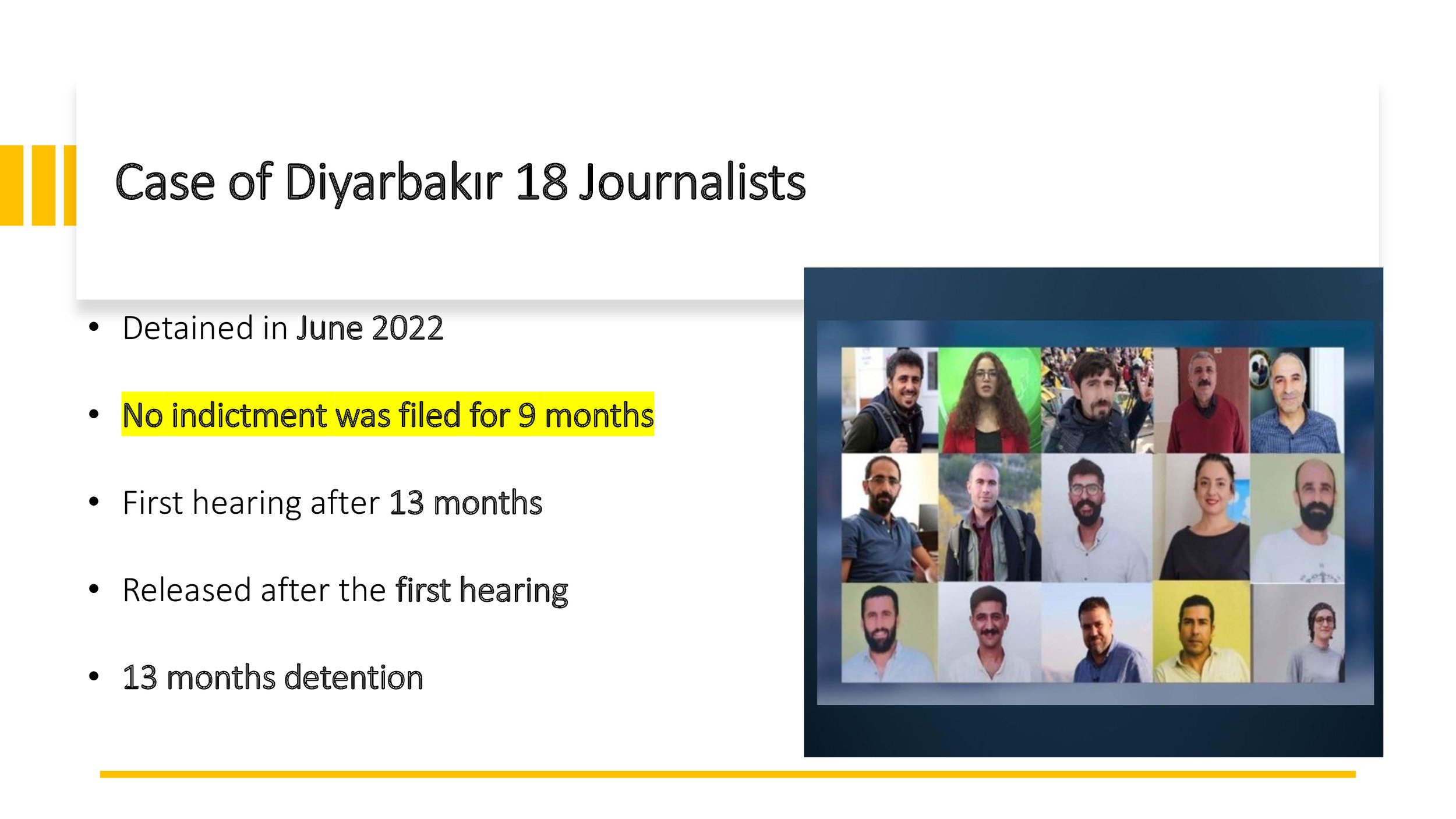
18 Journalists in Diyarbakır have been detained in June 2022, without an indictment being filed for 9 months. They were released after 13 months of detention.
MLSA and Hafiza Merkezi provided their Recommendations to the Committee of Ministers to:
Continue to examine the execution of the judgments in these case groups regularly and under enhanced procedure;
Examine and address the increasing use of interchangeable criminal provisions;
Instruct the Secretariat to draft an interim decision if no tangible progress is made or detailed statistics are not provided by the next review.
The NGOs called on Turkey to:
Amend its definition of terrorism in the Anti-Terrorism Law in a way that is narrowly construed and compliant with Convention standards;
Repeal or substantially amend Articles 125, 215, 216, 314 of the Criminal Code, and Articles 6 and 7 of Anti-Terrorism Law, particularly by addressing their overbroad, vague, and unforeseeable wording;
Abolish Articles 220 § 6, 220 § 7, 299 and 301 of the Criminal Code which fail to fulfill the legality criteria, and closely monitor the legal proposals on Article 220 § 6 as the Committee of Ministers;
Submit detailed and separate statistical information covering last 5 years of the application of different Articles causing freedom of expression violations;
Take tangible steps to ensure that the Anti-Terrorism Law and the Criminal Code are not interpreted in a broad manner by the judiciary, that pre-trial detention decisions are not used as a punitive measure, and that Constitutional Court judgements are promptly implemented by all judicial and administrative bodies;
Stop targeting, harassing and intimidating journalists and HRDs by subjecting them to judicial and administrative measures.
See slides for full briefing.
Relevant Documents:
NGO Communications
CM Decisions


































































































































































































![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-0.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438599541-LYSGVF2DTXHRE4WRUFE8/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-0.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-1.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438599788-8S3OR2Z7U6PE26121XE8/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-1.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-2.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438600567-KECVN9IAOW3EWN1THGZS/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-2.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-3.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438600758-GMJ5KQYQ8MNM1H43KZN6/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-3.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-4.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438601558-SKWWJALM9MB4791J2H6E/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-4.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-5.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438602251-WW7IBHLI1TNCZQ0ON7KZ/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-5.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-6.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438602515-0WOQMB95ZN93DST209TG/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-6.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-7.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438603213-3HYQW6MDVSY0OH3LHD7Y/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-7.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-8.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438603505-BD80YZ0E7CPYVFU0AQFR/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-8.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-9.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438604225-VN6ZM0WK6UYJSDBFDEOW/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-9.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-10.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438604435-6KTLCZ4M7SDUQ2VSEHYN/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-10.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-11.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438605177-BF9NGIGWO96ZURPYW6PI/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-11.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-12.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438605319-6Y41XXWHQAY717HNIGVZ/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-12.jpg)
![Baka_v_Hungary_20230227[6446]-13.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1677438606182-MKPUZHM3JZ45I718VTKA/Baka_v_Hungary_20230227%5B6446%5D-13.jpg)


















































![IDvM_Final[43]1024_1.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312659670-P7UOXBV9F2WE1HBXG8CM/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_1.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_2.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312659779-4J3152LHLLE24021SU5U/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_2.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_3.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312660324-RN6HZ3MVKBSRT2WVD0OA/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_3.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_4.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312660683-8P9Y0ZMSXTBB8M0B8SMQ/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_4.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_5.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312660939-QTS1VE1YMBQ1WGZI677G/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_5.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_6.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312661330-KIOW6KFXRU7GNVJ5I648/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_6.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_7.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312661753-B7NJLRYLJ6BK9EB0XHS7/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_7.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_8.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312661987-EEMHPPEQ0W2IO6R4AOAL/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_8.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_9.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312662426-TRVV0MZJ658ZG3WS6VY0/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_9.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_10.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312662678-9RW8YABBTHIVCXL1IRG5/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_10.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_11.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312663081-732YQ33632AKJV3Q0PQA/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_11.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_12.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312663436-CV1T29URTI29P1TH05J4/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_12.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_13.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312663712-UXRPIGHNQ5PUEDV8YZFD/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_13.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_14.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312664495-8EYGJQ43B8QQS497FYH6/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_14.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_15.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312664721-RIWUJ10IWTNE9W4PW1MY/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_15.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_16.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312665187-Y5BFI9P331IGWJ9G0DPJ/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_16.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_17.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312665540-OED4RWH1JBHRQXXH6WH5/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_17.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_18.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312665823-U5XCCRFJ2YF0YAMIMM78/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_18.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_19.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312666240-GE4THPOMXFMIQDSK5YJO/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_19.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_20.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312666568-0MCJH3IFAUBEP3VEFQK4/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_20.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_21.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312666849-488V1UBRD1500S9NBZMB/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_21.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_22.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312667194-XOF1I6XM863ED9IWMFM2/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_22.jpg)
![IDvM_Final[43]1024_23.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663312667642-P2KO4231PSVNNJNEY2CL/IDvM_Final%5B43%5D1024_23.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-0.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268133110-9R91RUEBJXBEH9QCQFKW/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-0.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-1.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268133177-DPUBS0WHRCFAANBHR1DY/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-1.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-2.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268133852-I8AT9N9NG6WKHOETR4VV/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-2.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-3.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268133981-6O1EY1HKRI9LHBYLS06D/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-3.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-4.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268134683-S08H5T010OC1HGL9S5O2/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-4.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-5.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268134800-E57KM91UGFDGFPXLP5LE/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-5.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-6.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268135511-LCV7KGZ4LWIZJ6M2TIZV/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-6.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-7.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268135551-5GSI4I40224PFKV3NZXQ/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-7.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-8.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268136132-2AMGOTLQPD4ZOLXH59O8/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-8.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-9.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268136274-SE7MYQZZI7LIT2R188NB/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-9.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-10.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268136820-NV18EUVT0R3D2UEVQW8J/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-10.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-11.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268136945-BRJRYJ4YQYKVB8ZFCWQI/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-11.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-12.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268137456-WG6MXB8L0X9D96PXOLSO/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-12.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-13.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268137735-R3YSZMAXEQBQY8F7R5AL/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-13.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-14.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268138076-CCDIZHL0WEOJNYLADCC6/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-14.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-15.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268138391-RQV9TO0LZVVC875UGR5I/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-15.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-16.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268138760-6U8RR746CQ5IQMYV8KC3/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-16.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-17.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268139051-6WUW67F0GSYLLO64S8K8/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-17.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-18.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268139697-3DWKKQFU4G3JYT6L6BQQ/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-18.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-19.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268139871-ZDPMQCSRPQ37O8N64KD1/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-19.jpg)
![20220914_Skendžić and Krznarić group -ENv2[75] - Read-Only-20.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663268140267-P9FXP7JAFPS23TQBEB3D/20220914_Skendz%CC%8Cic%CC%81+and+Krznaric%CC%81+group+-ENv2%5B75%5D+-+Read-Only-20.jpg)

![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-0.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267898413-VZE6ITQEX11X2K6JARV9/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-0.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-1.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267898428-1UIXENO8HAHMBJQJXEIM/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-1.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-2.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267899064-VP24SP9JG0FWDY8N04GC/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-2.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-3.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267899395-1P1CAA08DGIIJ0PVVFP7/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-3.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-4.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267900059-X59B8JEUB8EOLVK6GDN1/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-4.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-5.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267900175-8BKM28CHB4ASYXNCERX6/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-5.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-6.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267900982-CWUX0UIV87Z25T15VCTM/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-6.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-7.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267901167-M03GBSVU0IB7V7YJQ40H/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-7.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-8.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267901810-7KV7LQJLTJCN1KSBYA1H/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-8.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-9.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267901885-S5HVDUD90YDBEJMJSGNN/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-9.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-10.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267902543-KQ4BQ17CWEJ03ZS5UNKR/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-10.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-11.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267902685-1U6ZCJ3I4B335QESMJFN/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-11.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-12.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267903327-NYD1YOQIK22WUYSG3S05/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-12.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-13.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267903470-YPGXCG5NF89S4QIWX7IC/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-13.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-14.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267904014-6K4RT9RXDYYA4BE149VG/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-14.jpg)
![Ilias and Ahmed (1)[85]-15.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663267904186-3AUU56MWNTT7CCG1YP6D/Ilias+and+Ahmed+%281%29%5B85%5D-15.jpg)
![Demirtaş - CoM briefing 16.09.22[12] - Read-Only-0.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663270546758-8MNOPZMT9NDT581P6ABM/Demirtas%CC%A7+-+CoM+briefing+16.09.22%5B12%5D+-+Read-Only-0.jpg)
![Demirtaş - CoM briefing 16.09.22[12] - Read-Only-1.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663270547027-EFNJQWCAWYSHIE7B6F66/Demirtas%CC%A7+-+CoM+briefing+16.09.22%5B12%5D+-+Read-Only-1.jpg)
![Demirtaş - CoM briefing 16.09.22[12] - Read-Only-2.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663270547811-MQXY9VGBRKDSAO5V5O3I/Demirtas%CC%A7+-+CoM+briefing+16.09.22%5B12%5D+-+Read-Only-2.jpg)
![Demirtaş - CoM briefing 16.09.22[12] - Read-Only-3.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663270547915-J6FAYNVIY7V23B5X2JJG/Demirtas%CC%A7+-+CoM+briefing+16.09.22%5B12%5D+-+Read-Only-3.jpg)
![Demirtaş - CoM briefing 16.09.22[12] - Read-Only-4.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663270548597-POCBJXTOPWO5M8TOCANB/Demirtas%CC%A7+-+CoM+briefing+16.09.22%5B12%5D+-+Read-Only-4.jpg)
![Demirtaş - CoM briefing 16.09.22[12] - Read-Only-5.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663270548813-FZLM30NCY36PJ65ZMFCS/Demirtas%CC%A7+-+CoM+briefing+16.09.22%5B12%5D+-+Read-Only-5.jpg)
![Demirtaş - CoM briefing 16.09.22[12] - Read-Only-6.jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55815c4fe4b077ee5306577f/1663270549322-B30ODKL3WS1H9MMX30NT/Demirtas%CC%A7+-+CoM+briefing+16.09.22%5B12%5D+-+Read-Only-6.jpg)